
Welcome to The UW Shoulder Site @ uwshoulder.com
Please note that information on this site was NOT authored by Dr. Frederic A Matsen III and has not been proofread or intended for general public use. Information was intended for internal use only and is a compilation for random notes and resources.
If you are looking for medical information about the treatment of shoulders, please visit shoulderarthritis.blogspot.com for an index of the many blog entries by Dr. Frederick A Matsen III.
Cofield Shoulder Prostheses
Smith & Nephew Cofield Total Shoulder System
  |
 |
| Monoblock Cofield 1
Monoblock and modular total shoulder arthroplasty for osteoarthritis |
Thomas H Berquist. Imaging atlas of orthopedic appliances and prostheses. New York : Raven Press, 1995. |
This prosthesis is very similar to the Neer prostheses but the anterior fin's inferior edge is not lower than the inferior edge of the dorsal fin. Note flattened underside of head with sharp edge. Also note pointed tip of stem commonly found on Xryas of Cofield prostheses.
      |
|
| Cofield (Smith and Nephew), Shoulder Hemiarthroplasty for Glenohumeral Arthritis Associated with Severe Rotator Cuff Deficiency |
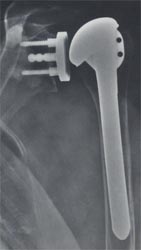
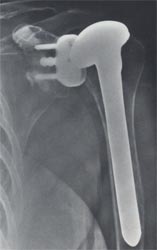
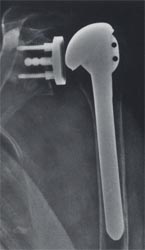
Thomas H Berquist. Imaging atlas of orthopedic appliances and prostheses. New York : Raven Press, 1995.

Resurfacing of the Glenoid in Total Shoulder Arthroplasty. A Comparison, at a Mean of Five Years, of Prostheses Inserted with and without Cement
Note the distinctive metal backed Cofiled Gleniod component that is sometimes present with Cofield humeral implants
  |
| Reimplantation of a Glenoid Component Following Component Removal and Allogenic Bone-Grafting |
 |
| smooth-textured Neer-II (3M);
Cofield tissue-ingrowth component (Smith and Nephew); Bio-Modular light and medium textured stem (Biomet) Damian M. Rispoli, John W. Sperling, George S. Athwal, Cathy D. Schleck, and Robert H. Cofield. Humeral Head Replacement for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am., Dec 2006; 88: 2637 - 2644. |
  |
| Prosthesis Not Confirmed
Periprosthetic Humeral Fractures After Shoulder Arthroplasty |
  |
|
| Kirschner Neer or Cofield
Revision Total Shoulder Arthroplasty for the Treatment of Glenoid Arthrosis |
  |
|
| Model Not Confirmed
Failure of an Implant after Total Shoulder Arthroplasty. A Case Report |






Periprosthetic Humeral Fractures After Shoulder Arthroplasty
Not Confirmed

Sperling JW et al. Infection after shoulder arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 2001
Smith & Nephew Cofield II Total Shoulder System
 |
 |
  |
 |
| Modular Cofield 2
Monoblock and modular total shoulder arthroplasty for osteoarthritis |
The hole in ventral fin distinguishes the Cofield II it from a Neer or Zimmer BF prosthesis.
Note - hole and fin configurations are very similar to the Zimmer Total Shoulder II monoblock system. The Cofield differs in that it has a pointed distal stem, a ridge/rim under the head and often has a notch/space under the head just superior to dorsal fin. The inferior edge of the ventral fin in the Cofield 2 isn't more inferior than the inferior edge of the dorsal fin as it is in the Zimmer Total Shoulder II. Except for the hole in the ventral find, the Zimmer Total Shoulder 2 has a ventral fin more similar in shape to that of a Neer 2 prosthesis.
 |
     |
|
| Prosthesis No Confirmed
The Use of the Reverse Shoulder Prosthesis for the Treatment of Failed Hemiarthroplasty for Proximal Humeral Fracture |
Prosthesis Not Confirmed
Periprosthetic Humeral Fractures After Shoulder Arthroplasty |
  |
|
| anterior subluxation
Kirschner Neer or Cofield Shoulder Arthroplasty for Arthritis After Instability Surgery |
 |
| Model Not Confirmed
Cofield (Smith and Nephew), Neer (3M) or Bio-Modular
(Biomet)
|
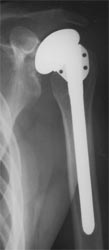  |
  |
| Appears to be Cofield 2
glenoid arthrosis and superior subluxation of the humeral head. Shoulder Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis Secondary to Glenoid Dysplasia |
Appears to be Cofield 2
bone-grafting and implantation of a glenoid component Shoulder Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis Secondary to Glenoid Dysplasia |





Periprosthetic Humeral Fractures After Shoulder Arthroplasty










































