Neuroscience For Kids
He Brains, She Brains

 Bigger - Stronger - Faster...are
there really any differences
between female brains and male brains? Differences between the brains of
men and women have generated considerable scientific and public interest.
If there are differences in the way that men and women behave, then it is
reasonable to suppose that their brains have something to do these
behavioral differences. Just what are these differences and where in the
brain might these differences be located?
Bigger - Stronger - Faster...are
there really any differences
between female brains and male brains? Differences between the brains of
men and women have generated considerable scientific and public interest.
If there are differences in the way that men and women behave, then it is
reasonable to suppose that their brains have something to do these
behavioral differences. Just what are these differences and where in the
brain might these differences be located?

 For hundreds of years, scientists have searched for
differences between the brains of men and women. Early research showing
that male brains were larger than female brains was used to "prove" that
male brains were superior to female brains. Of course, this "proof" is
NOT so simple and straight forward as you
will see. Nevertheless, even today, there is plenty of controversy about
the differences in the brains of men and women. Not only from an
anatomical point of view, but also from a functional point of view - in
other words, just what do the differences in the brains mean?
For hundreds of years, scientists have searched for
differences between the brains of men and women. Early research showing
that male brains were larger than female brains was used to "prove" that
male brains were superior to female brains. Of course, this "proof" is
NOT so simple and straight forward as you
will see. Nevertheless, even today, there is plenty of controversy about
the differences in the brains of men and women. Not only from an
anatomical point of view, but also from a functional point of view - in
other words, just what do the differences in the brains mean?
Hormones that are present during a baby's development will affect the brain and determine whether the brain will be female or male. Studies that have looked at differences in the brains of males and females have focused on:
- Total Brain Size
- The Corpus Callosum
- The Hypothalamus
Differences in Total Brain Size?
 Almost all studies show
that at birth, a boy's brain is bigger than a girl's brain. At birth, the
average brain of boys is between 12-20% larger than that of girls. The
head circumference of boys is also larger (2%) than that of girls.
However, when the size of the brain is compared to body weight at this
age, there is almost no difference between boys and girls. So, a girl
baby and a boy baby who weigh the same will have similar brain sizes.
Almost all studies show
that at birth, a boy's brain is bigger than a girl's brain. At birth, the
average brain of boys is between 12-20% larger than that of girls. The
head circumference of boys is also larger (2%) than that of girls.
However, when the size of the brain is compared to body weight at this
age, there is almost no difference between boys and girls. So, a girl
baby and a boy baby who weigh the same will have similar brain sizes.
In adults, the average brain weight in men is about 11-12% MORE than the average brain weight in women. Men's heads are also about 2% bigger than women's. Remember though, men on average weigh more than women and that absolute brain size may not be the best measure of intelligence. Many behavioral differences have been reported for men and women. For example, it has been said that women are better in certain language abilities and men are better in certain spatial abilities. Many studies have tried to find differences in the right and left cerebral hemispheres to suggest that male and female brains are different. However, few of these experiments have found meaningful differences between men and women. If fact, there are many similarities between the cerebral hemispheres of men and women.
Brain Weights
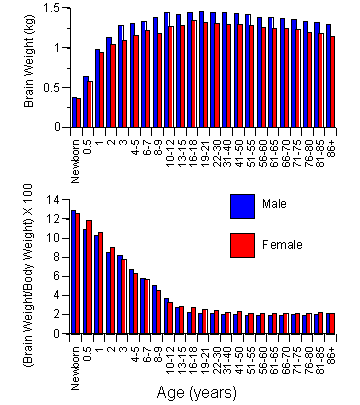
Data from Dekaban, A.S. and Sadowsky, D., Changes in brain weights during
the span of human life:
relation of brain weights to body heights and body weights, Ann.
Neurology, 4:345-356, 1978)
Differences in the Corpus Callosum?
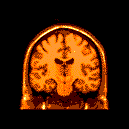
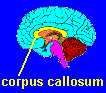 The major pathway that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is
called the corpus callosum. (The corpus callosum is the fiber tract made
up of 200-250 million axons that is cut in split
brain patients.) Some claims have been made that the corpus callosum
is bigger and more developed in women than in men. These claims have even
been reported in the popular media (Time Magazine, Jan. 20, 1992,
pp. 36-42; Newsweek Magazine, March 27, 1995, pp. 51). However,
other studies have told a different story. Using magnetic resonance imaging methods, some researchers have
found no differences in the size of the corpus callosum of men and women
or that the corpus callosum is larger in men than in women (Allen et al.,
2003).
The major pathway that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is
called the corpus callosum. (The corpus callosum is the fiber tract made
up of 200-250 million axons that is cut in split
brain patients.) Some claims have been made that the corpus callosum
is bigger and more developed in women than in men. These claims have even
been reported in the popular media (Time Magazine, Jan. 20, 1992,
pp. 36-42; Newsweek Magazine, March 27, 1995, pp. 51). However,
other studies have told a different story. Using magnetic resonance imaging methods, some researchers have
found no differences in the size of the corpus callosum of men and women
or that the corpus callosum is larger in men than in women (Allen et al.,
2003).
Differences in the Hypothalamus?
The hypothalamus is one area of the brain with well-documented differences between men and women. Two areas of the hypothalamus, the preoptic area and the suprachiasmatic nucleus, have clear differences in female and male brains.
 Preoptic Area of the
Hypothalamus: This area of the
hypothalamus is involved in mating behavior.
In males of several species including humans, the preoptic area is greater
in volume, in cross-sectional area and in the number of cells. In men,
this area is about 2.2 times larger than in women and contains 2 times
more cells. Apparently, the difference in this area is only apparent
after a person is 4 years old. At 4 years of age, there is a decrease in
the number of cells in this nucleus in girls. The exact
function of this nucleus in behavior is not fully known.
Preoptic Area of the
Hypothalamus: This area of the
hypothalamus is involved in mating behavior.
In males of several species including humans, the preoptic area is greater
in volume, in cross-sectional area and in the number of cells. In men,
this area is about 2.2 times larger than in women and contains 2 times
more cells. Apparently, the difference in this area is only apparent
after a person is 4 years old. At 4 years of age, there is a decrease in
the number of cells in this nucleus in girls. The exact
function of this nucleus in behavior is not fully known.
 Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
of the Hypothalamus: This area of the hypothalamus is involved with
circadian rhythms and reproduction cycles. The only difference between
women and men in this area is one of shape: in males, this nucleus is
shaped like a sphere; in females it is more elongated. However, the
number of cells and volume of this nucleus are not different in men and
women. It is possible that the shape of the suprachiasmatic
nucleus influences the connections that this area makes with other areas
of the brain, especially the other areas of the hypothalamus.
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
of the Hypothalamus: This area of the hypothalamus is involved with
circadian rhythms and reproduction cycles. The only difference between
women and men in this area is one of shape: in males, this nucleus is
shaped like a sphere; in females it is more elongated. However, the
number of cells and volume of this nucleus are not different in men and
women. It is possible that the shape of the suprachiasmatic
nucleus influences the connections that this area makes with other areas
of the brain, especially the other areas of the hypothalamus.
Women and Men - Boys and Girls
The behavioral and neurological differences between men and women require further study. Perhaps new studies will find neuroanatomical differences that explain some of the complex differences between male and female behavior. However, from a review of the current scientific evidence, it appears that differences in many cognitive behaviors (for example, memory) are related more to individual differences between people than to whether people are female or male.
 Hear IT! |
Hypothalamus | Corpus Callosum |
More about the possible differences between male and female brains:
- "His Brain, Her Brain" by Larry Cahill in Scientific American, May, 2005.
- Brain imaging study of spatial memory
- Allen, J.S., Damasio, H., Grabowskia, T.J., Brussa, J. and Zhang, W., Sexual dimorphism and asymmetries in the gray?white composition of the human cerebrum, NeuroImage, 18:880-894, 2003.
Copyright © 1996-2015, Eric H. Chudler All Rights Reserved.