Neuroscience For Kids
New Treatment for Huntington's Disease
August 18, 2008
 This month, the US Food and Drug
Administration approved the first drug (Xenazine; tetrabenazine) to
treat people with Huntington’s disease (HD). Xenazine is used to reduce
the jerky, involuntary movements in people with this disease.
This month, the US Food and Drug
Administration approved the first drug (Xenazine; tetrabenazine) to
treat people with Huntington’s disease (HD). Xenazine is used to reduce
the jerky, involuntary movements in people with this disease.
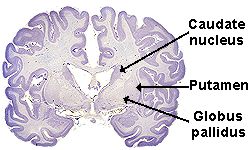 HD is a relatively rare disease, affecting approximately 30,000 people in
the US. HD is an inherited neurological disorder: if either parent has
it, his or her child has a 50-50 chance of getting it. Symptoms, which
usually appear after age 30, include dementia (poor judgment, memory
problems, personality changes), chorea (jerky, random movements of the
body), poor coordination, depression, and mood swings. Patients often die
within 15 years of the onset of symptoms. HD damages neurons in the area
of the brain called the basal ganglia, especially the caudate nucleus and
globus pallidus. People with HD have overactive dopamine neurotransmitter systems.
HD is a relatively rare disease, affecting approximately 30,000 people in
the US. HD is an inherited neurological disorder: if either parent has
it, his or her child has a 50-50 chance of getting it. Symptoms, which
usually appear after age 30, include dementia (poor judgment, memory
problems, personality changes), chorea (jerky, random movements of the
body), poor coordination, depression, and mood swings. Patients often die
within 15 years of the onset of symptoms. HD damages neurons in the area
of the brain called the basal ganglia, especially the caudate nucleus and
globus pallidus. People with HD have overactive dopamine neurotransmitter systems.
Xenazine works by blocking the uptake of the neurotransmitter dopamine into vesicles. Therefore, there is a decrease in the amount of dopamine available to be released into synapses. Side effects of Xenazine include insomnia, depression, drowsiness, restlessness and nausea.
References and further information:
- Xenazine - Announcement
- FDA Press Release
- Huntington's Disease - Hope through Research: from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
- Huntington's Disease Association of England
- Huntington's Disease Society of America
- A Video Introduction to the Basics of Huntington’s Disease
Copyright © 1996-2008, Eric H. Chudler, University of Washington