Research
Overall Lab Mission
The Averkiou Lab develops new ultrasound imaging and therapy technology for cancer and heart diseases. Using advanced nonlinear imaging techniques and microbubble contrast agents, we develop ways to image the microcirculation in order to detect the earliest stages of tumor angiogenesis and atherosclerosis, and closely monitor their treatment. We also use the unique properties of ultrasound and microbubbles to improve the delivery of drugs into cancer cells. The lab focuses on transferring innovations from preclinical research into clinical use.
Perfusion Quantification
We develop ultrasound imaging techniques to image and quantify blood flow in the microcirculation. These techniques are based on the nonlinear oscillations of microbubbles that result from exposure to ultrasound. We can detect and characterize tumors based on their microvascular patterns while we also develop quantitative techniques to monitor the outcomes of therapies targeting angiogenesis. Clinical applications include liver, breast, kidney and prostate cancer. With the support of Quantitative Imaging Biomarkers Alliance (QIBA), we currently work with industry partners in developing a standarized perfusion quantification protocol for multi-center clinical trials. We also work with physician-scientists in UW Radiology to develop a contrast-enhanced ultrasound based technique for liver lesion evaluation. QIBA is a part of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Selected publications:
- Krolak C, Wei A, Shumaker M, Dighe M, Averkiou M. "A Comprehensive and Repeatable Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Quantification Approach for Clinical Evaluations of Tumor Blood Flow". Invest Radiol. 2024 Oct 18. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000001127. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 39418656.
- Krolak C, Dighe M, Clark A, Shumaker M, Yeung R, Barr RG, Kono Y, Averkiou M. "Quantification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Vascular Dynamics With Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound for LI-RADS Implementation". Invest Radiol. 2023 Sep 19. PMID: 37725492.
- Check out this article about the impacts of the Averkiou Lab's CEUS research in UW BioE's "Hope and Healing".
- Check out Connor Krolak's Seattle Town Hall public science talk about quantification of clinical hepatocellular carcinoma contrast-enhanced ultrasound data here
- Monsky W, Keravnou C, Averkiou M. "Contrast-enhanced ultrasound to ultrasound fusion during microwave ablation: feasibility study in a perfused porcine liver model". J Ultrasound. 2019 Feb 27.
- Averkiou MA, Keravnou CP, Izamis ML, Leen E. "Evaluation of Perfusion Quantification Methods with Ultrasound Contrast Agents in a Machine-Perfused Pig Liver". Ultraschall Med. 2016 May 3.
- Christofides D, Leen E, Averkiou M. "Evaluation of the accuracy of liver lesion DCEUS quantification with respiratory gating". IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2015 Oct 7.
- Dietrich CF, Averkiou MA, Correas JM, Lassau N, Leen E, Piscaglia F. "An EFSUMB introduction into Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (DCE-US) for quantification of tumour perfusion". Ultraschall Med. 2012 Aug;33(4):344-51.
- Leen E, Averkiou M, Arditi M, Burns P, Bokor D, Gauthier T, Kono Y, Lucidarme O. "Dynamic contrast enhanced ultrasound assessment of the vascular effects of novel therapeutics in early stage trials". Eur Radiol. 2012 Jul;22(7):1442-50.
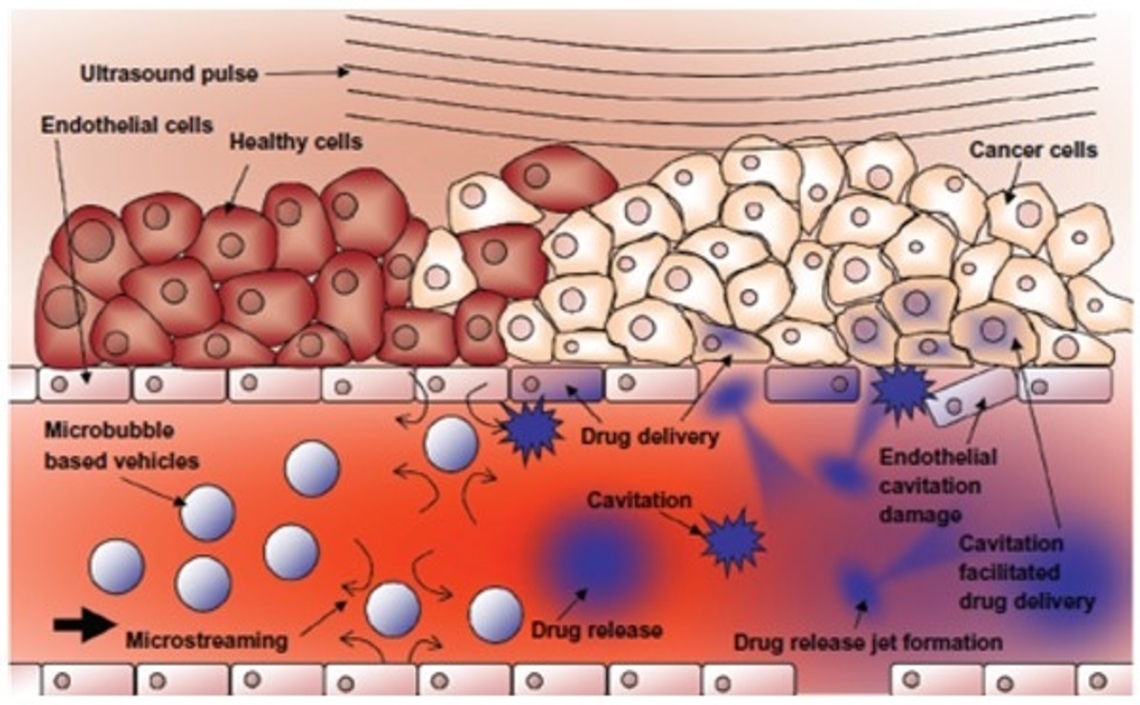
Ultrasound mediated drug delivery
Drugs may be selectively delivered in spatially controlled areas under image-guidance with either temperature or pressure stimuli generated by ultrasound. Recent work in the lab has sought to understand the mechanism of ultrasound-mediated vascular changes and drug delivery and optimize methods for image-guided interventions. We use in vitro (cells, microvascular networks), ex vivo (machine perfused pig livers), and in vivo (mice, pigs) setups to study the physical interactions of ultrasound-driven microbubbles in biological systems.
Selected publications:
- Juang EK, De Koninck LH, Vuong KS, Gnanaskandan A, Hsiao CT, Averkiou MA. "Controlled Hyperthermia With High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound and Ultrasound Contrast Agent Microbubbles in Porcine Liver.". Ultrasound Med Biol. 2023 Aug;49(8):1852-1860. PMID: 37246049; PMCID: PMC10330369.
- Check out Lance De Koninick's Seattle Town Hall public science talk about ultrasound mediated drug delivery with microbubble contrast agents here
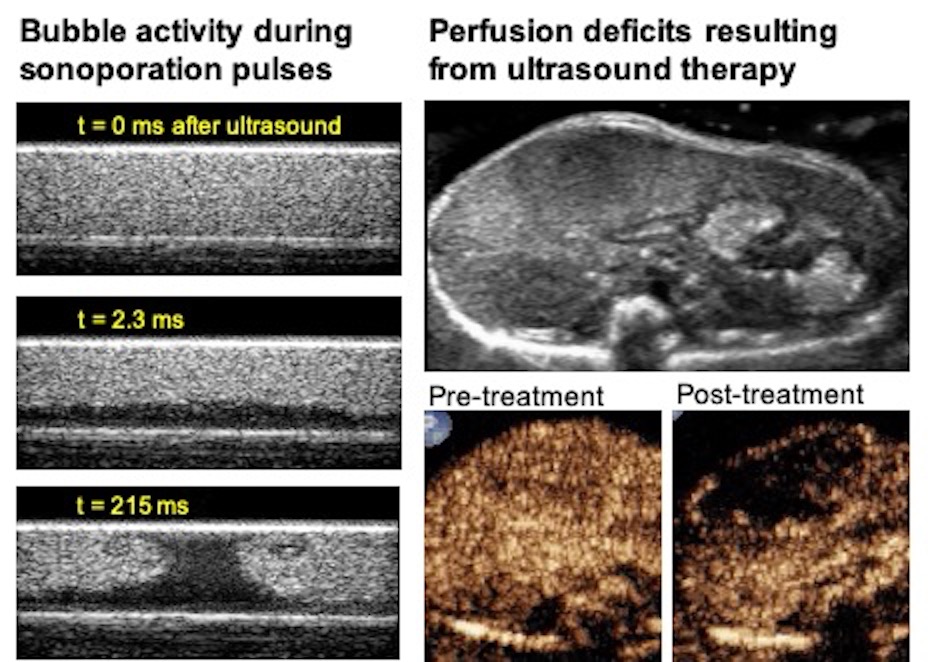
- Keller S, Bruce M, Averkiou MA. "Ultrasound Imaging of Microbubble Activity during Sonoporation Pulse Sequences". Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019 Mar;45(3):833-845.
- Juang EK, De Cock I, Keravnou C, Gallagher MK, Keller SB, Zheng Y, Averkiou M. "Engineered 3D microvascular networks for the study of ultrasound-microbubble-mediated drug delivery". Langmuir. 2018 Dec 12.
- Keravnou CP, De Cock I, Lentacker I, Izamis ML, Averkiou M. "Microvascular injury and perfusion changes induced by ultrasound and microbubbles in a machine-perfused pig liver". Ultrasound in Med. & Biol, Vol. 42, No. 11, pp. 2676–2686, November 2016.
- Mannaris C, Efthymiou E, Meyre ME, Averkiou MA. "In vitro localized release of thermosensitive liposomes with ultrasound-induced hyperthermia". Ultrasound Med Biol. 2013 Nov;39(11):2011-20.
- Mannaris C, Averkiou MA. "Investigation of microbubble response to long pulses used in ultrasound-enhanced drug delivery". Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012 Apr;38(4):681-91.
Microbubble-Enhanced Heating
High intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) is a noninvasive tool for targeted thermal ablation treatments. HIFU is used clinically for thermal ablation of various cancers and uterine fibroids. Additionally, it has applications in the brain for treatment of essential tremor, Parkinson’s disease, and neurological pain. Current HIFU treatments in the brain require very high acoustic intensities for treatment since a large amount of energy is absorbed or reflected by the skull. Additionally, with current technology, focused ultrasound is only capable of burning very small regions towards the center of the brain. Safely increasing the ablation zone and decreasing the acoustic intensity is necessary to treat a wider range of neurological disorders. Our work focuses on enhancing HIFU treatments in the brain by utilizing ultrasound contrast agents to better localize treatments and to decrease the acoustic energy required for thermal ablation.
Selected publications:
- Clark A, Bonilla S, Suo D, Averkiou M. “Enhanced heating with microbubbles in high intensity focused ultrasound applications” 25th European symposium on Ultrasound Contrast Imaging,Rotterdam, Netherlands, 2020.
- Suo D, Clark A, Bonilla S, Keller S, Averkiou M. “Controlled bubble-enhanced heating with added microbubbles” 19th Internarional Symposium of ISTU, Barcelona, Spain, 2019.
- Keller S, Bruce M, Averkiou M. “Ultrasound imaging of microbubble activity during sonoporation pulse sequences” Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology, 45(3), 833-845, 2019.
- Suo D, Juang E, Keller S, Pitts C, Averkiou M. “Image-guided, bubble-enhanced thermal ablation” 24th European symposium on Ultrasound Contrast Imaging, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 2019.
- Suo D, Juang E, Keller S, Averkiou M. “Real-time imaging-guided microbubble mediated high intensity focused ultrasound heating in an ex-vivo machine-perfused pig liver” 176th ASA conference, Victoria, BC, 2018.
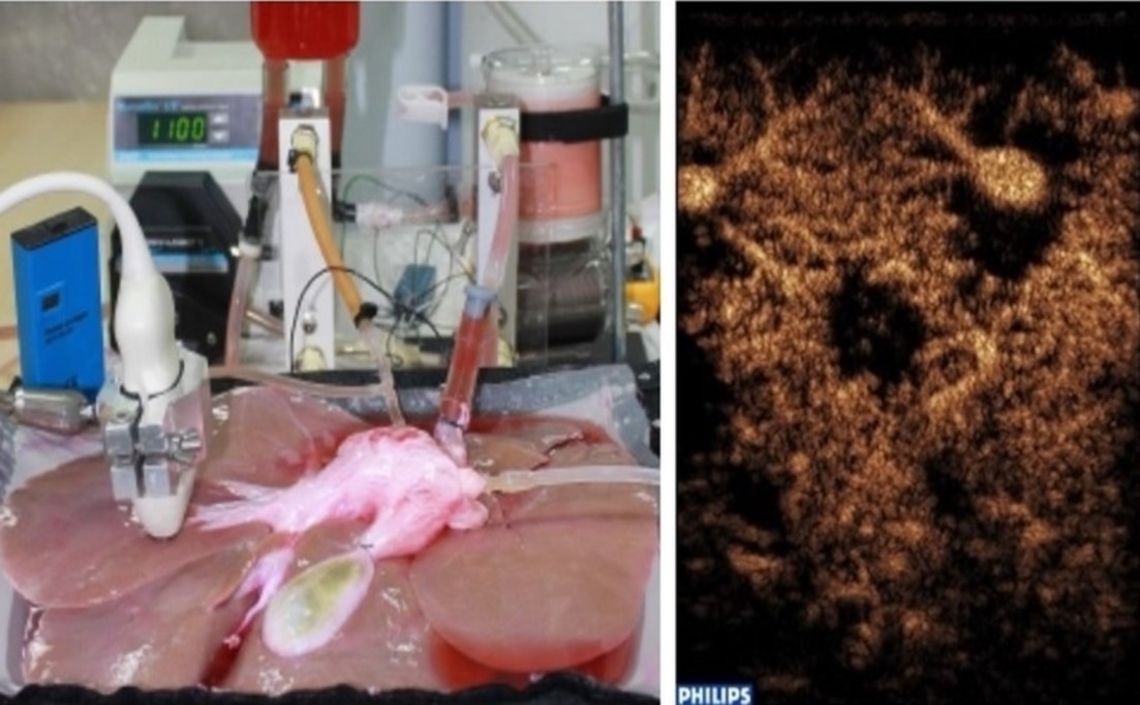
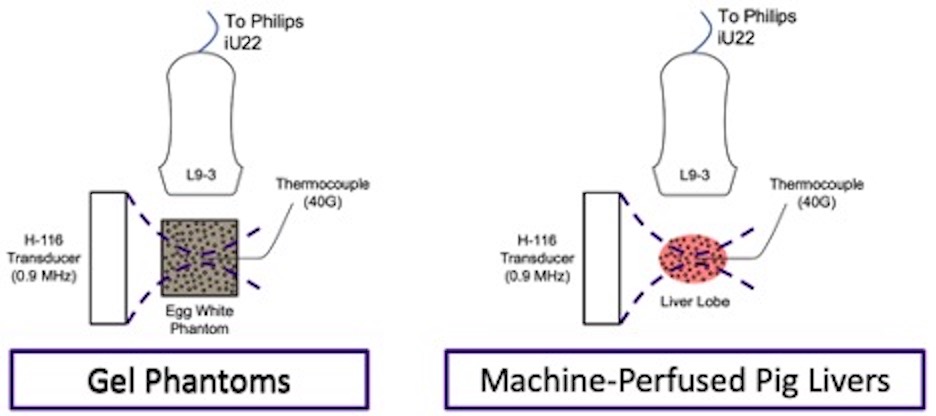
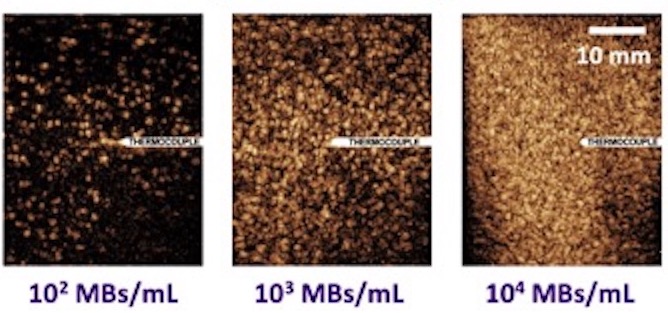
Ex-vivo machine perfusion of human-sized livers
One unique research tool of the Averkiou lab is the ex-vivo machine perfused (MP) pig liver phantom. MP functions as an artificial body with a wholly- or partially-artificial blood supply to sustain an isolated organ (typically from slaughterhouse animals) ex-vivo. MP presents a very promising platform for quantification of blood flow in the microcirculation which is a key element in cancer therapy monitoring. MP is also a test bed for therapeutic applications of ultrasound, such as ultrasound mediated drug delivery, and thermal ablation.
Selected publications:
- Izamis ML, Efstathiades A, Keravnou C, Leen EL, Averkiou MA. "Dynamic contrast-enhanced ultrasound of slaughterhouse porcine livers in machine perfusion". Ultrasound Med Biol. 2014 Sep;40(9):2217-30.
- Izamis ML, Efstathiades A, Keravnou C, Georgiadou S, Martins PN, Averkiou MA. "Effects of air embolism size and location on porcine hepatic microcirculation in machine perfusion". Liver Transpl. 2014 May;20(5):601-11.
- Keravnou CP, De Cock I, Lentacker I, Izamis ML, Averkiou M. "Microvascular injury and perfusion changes induced by ultrasound and microbubbles in a machine-perfused pig liver". Ultrasound in Med. & Biol, Vol. 42, No. 11, pp. 2676–2686, November 2016.
- Averkiou MA, Keravnou CP, Izamis ML, Leen E. "Evaluation of Perfusion Quantification Methods with Ultrasound Contrast Agents in a Machine-Perfused Pig Liver". Ultraschall Med. 2016 May 3.
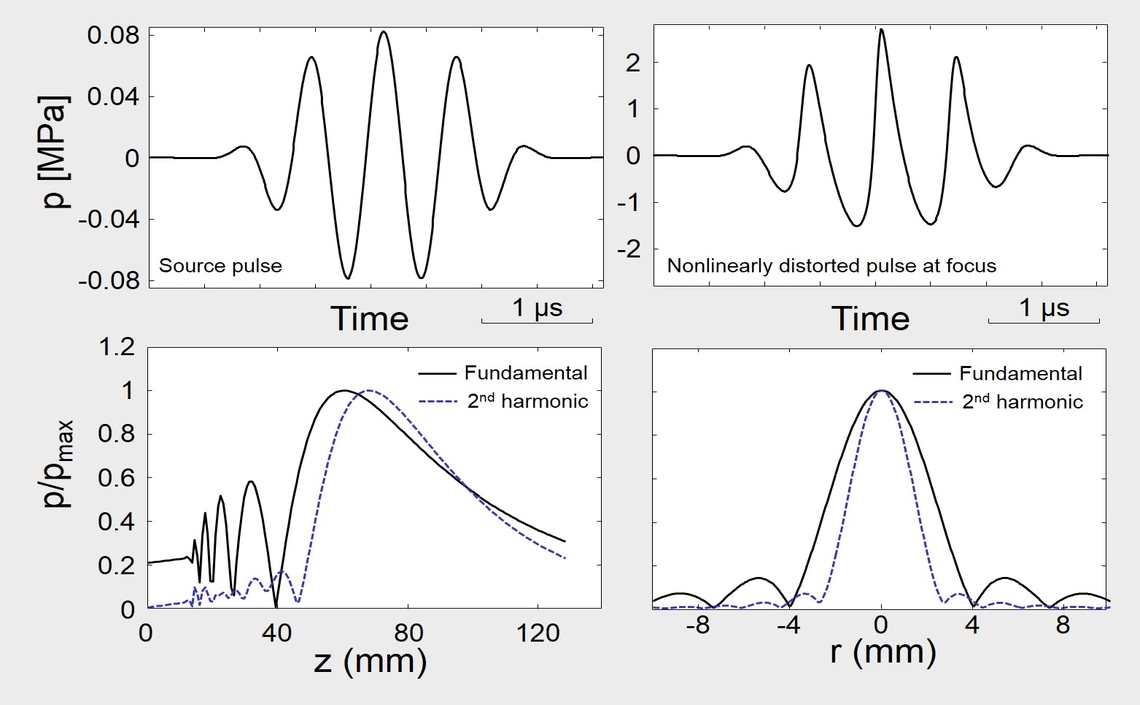
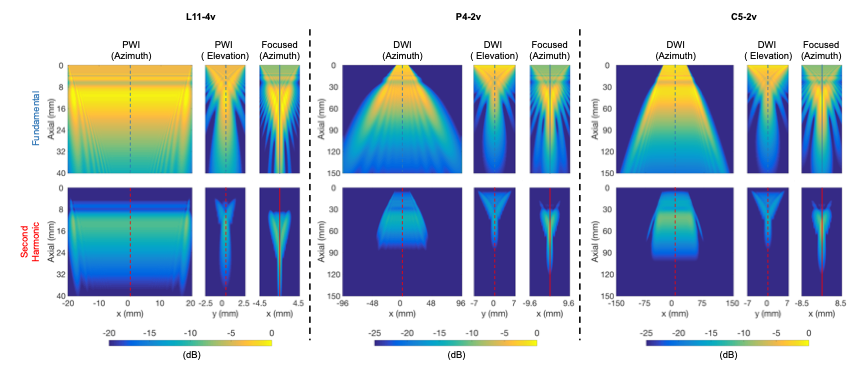
Nonlinear propagation of ultrasound
We study ultrasound nonlinear propagation in tissue in order to develop new imaging approaches and other diagnostic tools in clinical areas like imaging large/obese patients and early detection of diffuse liver disease.
Selected publications:
- Lai TY, Bruce M, and Averkiou MA. "Modeling of the acoustic field produced by diagnostic ultrasound arrays in plane and diverging wave modes." IEEE transactions on ultrasonics, ferroelectrics, and frequency control 66.7 (2019): 1158-1169.
- Lai TY, et al. "Harmonic Generation in Tissue with Matrix Arrays for 4D Cardiac THI." 2019 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS). IEEE, 2019.
- Lai TY, and Averkiou MA. "The Linear and Nonlinear Ultrasound Field of Convex Arrays Operating in a Diverging Wave Mode." 2018 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS). IEEE, 2018.
- Keravnou CP, Averkiou MA. "Harmonic generation with a dual frequency pulse". J Acoust Soc Am. 2014 May;135(5):2545-52.
- Averkiou M. "Tissue harmonic ultrasonic imaging" in Optical and acoustical imaging of biological media, C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris, Applied Physics(Biophysiscs), t. 2, Serie IV, Elsevier, Paris, pp.1139-1151, 2001.
- Averkiou MA, Roundhill DN and Powers JE. "A new imaging technique based on the nonlinear properties of tissues" in Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Toronto, Canada, vol. 2, 1561-1566, 1997.
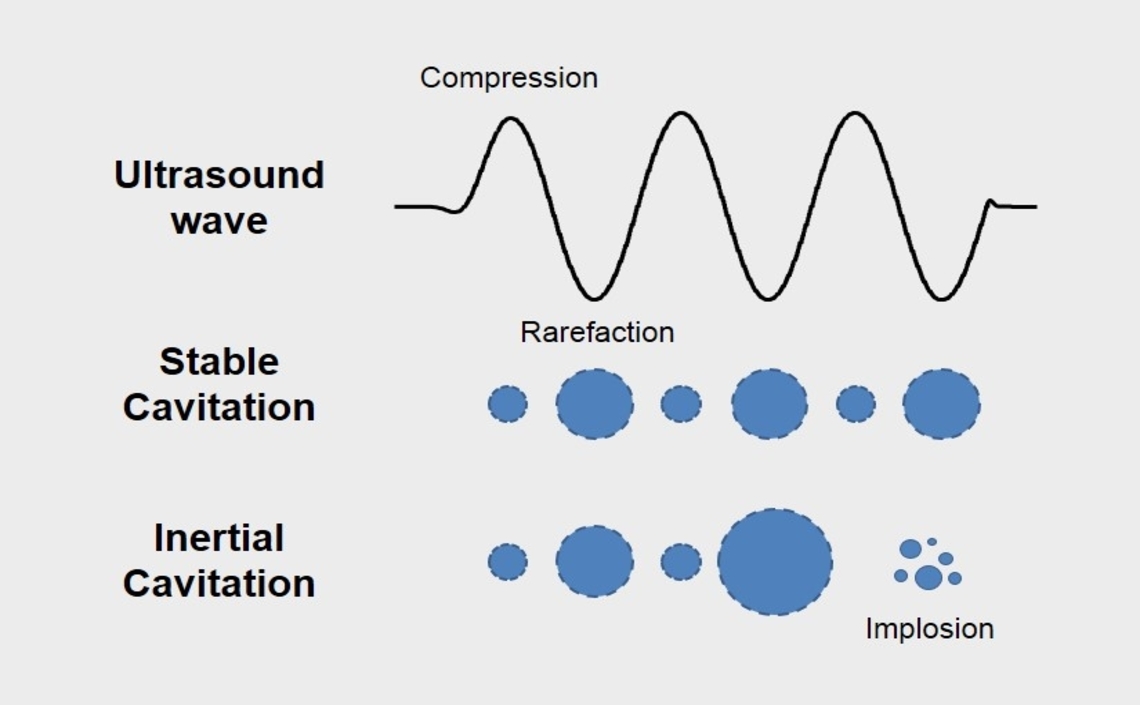
Bubble dynamics and response to ultrasound
Ultrasound contrast agents (UCAs) are micrometer-sized gas-filled bubbles stabilized with a lipid or polymeric shell. The high echogenicity of microbubbles compared with that of red blood cells is used to enhance image contrast in diagnostic ultrasound. The Averkiou Lab studies the nonlinear oscillations of microbubbles exposed to different ultrasound conditions in order to get an in-depth understanding of microbubble behavior and to further improve both diagnostic and therapeutic applications of contrast enhanced ultrasound. Microbubble dynamics is also very important when studying ultrasound-mediated drug delivery approaches. To this end, we have studied passive cavitation detection using clinical ultrasound systems and a variety of microbubble formulations and have also imaged the process of ultrasound insonation on microbubble activity. We have also explored the use of microbubbles to enhance heating in high-intensity focused ultrasound applications
Selected publications:
- Keller SB, Lai TY, De Koninck L, Averkiou MA. "Investigation of the phase of nonlinear echoes from microbubbles during amplitude modulation". IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2022 Jan 24
- Keravnou CP, Mannaris C, Averkiou MA. "Accurate measurement of microbubble response to ultrasound with a diagnostic ultrasound scanner". IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2015 Jan;62(1):176-84.
- Mannaris C, Averkiou MA. "Investigation of microbubble response to long pulses used in ultrasound-enhanced drug delivery". Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012 Apr;38(4):681-91.