Key concept: Parameters specified with the GIMP keyword determines the putative relationship between random mutational events and the onset of genomic instability.Tip: Combinations of PGH, PGA, and NCG that yield the same value for PGH*PGA*NCG produce approximately the same level of genomic instability and, ultimately, neoplastic transformation. The NCM parameter can have a dramatic effect on the shape of the cell transformation curve as a function of delivered dose (e.g., try NCM=1, 2 or 3).
|
Example 14.1 The random mutation events leading to genomic instability per surviving fraction (EGI/SF) and transformation frequency per survivor (TPS) for variations in the number of critical genes (NCG) (e.g., rmrsim8.inp -> rmrsim8.out).  Variation of EGI/SF with the absorbed single fraction radiation dose. Comments: The degree of genomic instability (represented by EGI/SF) increases with increasing absorbed dose and NCG. Variation of EGI/SF with the absorbed single fraction radiation dose. Comments: The degree of genomic instability (represented by EGI/SF) increases with increasing absorbed dose and NCG. 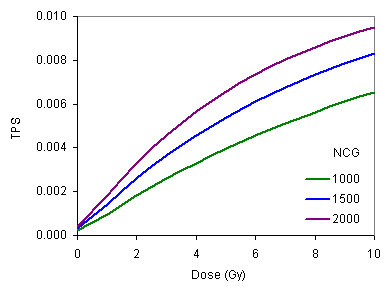 Variation of TPS with the absorbed single fraction radiation dose Comments: The behavior of transformation frequency per survivor (TPS) is similar to the degree of genomic instability shown in the previous figure. Suggested problems Variation of TPS with the absorbed single fraction radiation dose Comments: The behavior of transformation frequency per survivor (TPS) is similar to the degree of genomic instability shown in the previous figure. Suggested problems- Without performing any calculations (using the definitions of the terms), predict the trends of EGI/SF and TPS for increasing PGA, PGH and NCM.
- Appropriately modify and run the input file given in Example 14.1 to check your answers for Problem 1.
- Obtain the time variation of TPS is obtained after an acute single dose exposure of 6 Gy at10,000 Gy/h. Run your input file using VC, plot the results and elaborate.
- How different would the transformation frequency per survivor be if the same dose assumed in problem 3 is delivered as a split dose with a time gap of 10 hours? Assume the same dose rate.
|
|

