mmf.math.linalg.cholesky.se99¶
| se99(A) | A revised modified Cholesky factorisation algorithm. |
| eschol(A) | Here is a MATLAB translation of the same code: |
| modchol(A) | Notes |
| air_modchol(A) | This is based on the following c code from the `AIR project |
These are a collection of codes based on the [ES99] algorithm.
- mmf.math.linalg.cholesky.se99.se99(A)[source]¶
A revised modified Cholesky factorisation algorithm.
Schnabel, R. B. and Eskow, E. 1999, A revised modifed cholesky factorisation algorithm. SIAM J. Optim. 9, 1135-1148.
Notes
The invariant here is that at stage
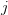 :
: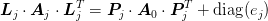
with the final stage
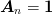 . We store
. We store 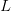 in the
lower portion of
in the
lower portion of 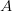 .
.
- mmf.math.linalg.cholesky.se99.eschol(A)[source]¶
Here is a MATLAB translation of the same code:: % /* % ** By Jeff Gill, April 2002. % ** % ** This procedure produces: % ** % ** y = chol(A+E), where E is a diagonal matrix with each element as small % ** as possible, and A and E are the same size. E diagonal values are % ** constrained by iteravely updated Gerschgorin bounds. % ** % ** REFERENCES: % ** % ** Jeff Gill and Gary King. 1998. “`Hessian not Invertable.’ Help!” % ** manuscript in progress, Harvard University. % ** % ** Robert B. Schnabel and Elizabeth Eskow. 1990. “A New Modified Cholesky % ** Factorization,” SIAM Journal of Scientific Statistical Computating, % ** 11, 6: 1136-58. % ** % ** % ** % ** Stephane Adjemian (2003): translation from Gauss to Matlab. % */ function AA = generalized_cholesky2(A)
n = size(A,1); L = zeros(n,n); deltaprev = 0; gamm = max(abs(diag(A))); tau = eps^(1/3);
- if min(eig(A)) > 0;
- tau = -1000000;
end;
norm_A = max(sum(abs(A))’); gamm = max(abs(diag(A))); delta = max([eps*norm_A;eps]); Pprod = eye(n);
- if n > 2;
- for k = 1,n-2;
- if min((diag(A(k+1:n,k+1:n))’ - A(k,k+1:n).^2/A(k,k))’) < tau*gamm ...
- & min(eig(A((k+1):n,(k+1):n))) < 0;
[tmp,dmax] = max(diag(A(k:n,k:n))); if A(k+dmax-1,k+dmax-1) > A(k,k);
P = eye(n); Ptemp = P(k,:); P(k,:) = P(k+dmax-1,:); P(k+dmax-1,:) = Ptemp; A = P*A*P; L = P*L*P; Pprod = P*Pprod;end; g = zeros(n-(k-1),1); for i=k:n;
- if i == 1;
- sum1 = 0;
- else;
- sum1 = sum(abs(A(i,k:(i-1)))’);
end;
- if i == n;
- sum2 = 0;
- else;
- sum2 = sum(abs(A((i+1):n,i))); end;
g(i-k+1) = A(i,i) - sum1 - sum2;
end; [tmp,gmax] = max(g); if gmax ~= k;
P = eye(n); Ptemp = P(k,:); P(k,:) = P(k+dmax-1,:); P(k+dmax-1,:) = Ptemp; A = P*A*P; L = P*L*P; Pprod = P*Pprod;end; normj = sum(abs(A(k+1:n,k))); delta = max([0;deltaprev;-A(k,k)+normj;-A(k,k)+tau*gamm]); if delta > 0;
A(k,k) = A(k,k) + delta; deltaprev = delta;end;
end; A(k,k) = sqrt(A(k,k)); L(k,k) = A(k,k); for i=k+1:n;
- if L(k,k) > eps;
- A(i,k) = A(i,k)/L(k,k);
- end;
- L(i,k) = A(i,k);
A(i,k+1:i) = A(i,k+1:i) - L(i,k)*L(k+1:i,k)’; if A(i,i) < 0;
A(i,i) = 0;end;
end;
end;
end; A(n-1,n) = A(n,n-1); eigvals = eig(A(n-1:n,n-1:n)); dlist = [ 0 ; deltaprev ;...
-min(eigvals)+tau*max((inv(1-tau)*max(eigvals)-min(eigvals))|gamm) ];- if dlist(1) > dlist(2);
- delta = dlist(1);
- else;
- delta = dlist(2);
end; if delta < dlist(3);
delta = dlist(3);end; if delta > 0;
A(n-1,n-1) = A(n-1,n-1) + delta; A(n,n) = A(n,n) + delta; deltaprev = delta;end; A(n-1,n-1) = sqrt(A(n-1,n-1)); L(n-1,n-1) = A(n-1,n-1); A(n,n-1) = A(n,n-1)/L(n-1,n-1); L(n,n-1) = A(n,n-1); A(n,n) = sqrt(A(n,n) - L(n,(n-1))^2); L(n,n) = A(n,n); AA = Pprod’*L’*Pprod’;
- mmf.math.linalg.cholesky.se99.modchol(A)[source]¶
Notes
Based on the MATLAB code from the Spatial Econometric Toolkit by James LeSage:
function [l,d]=modchol(A) % PURPOSE: Modified Cholesky algorithm of Elizabeth Eskow and Robert B. Schnabel % Performs a modified cholesky factorization % of a SYMMETRIC MATRIX A, of the form P'*A*P + d = L*L' % ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- % USAGE: [l,d] = modchol(A) % where: A = symmetric input matrix % L = cholesky matrix % d = the minimal diagonal increment according to the Gerschgorin Circle Theorem % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % NOTES: Useful for dealing with ill-conditioned numerical hessians and the like % Schnabel, R. B. and Eskow, E. 1990. "A New Modified Cholesky Factorization." % SIAM Journal of Scientific Statistical Computing 11, 1136-58.) % % Altman, M., J. Gill and M. P. McDonald. 2003. Numerical Issues in Statistical % Computing for the Social Scientist}. John Wiley \& Sons, has a nice % discussion of this and R-code for this algorithm at: % http://www.hmdc.harvard.edu/numerical_issues/ % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % Jim LeSage n=max(size(A)); gamma=max(abs(diag(A))); psi=max(max(abs(A-diag(diag(A))))); delta=eps*max(gamma+psi,1); Bet=sqrt( max([gamma,psi/sqrt(n^2-1),eps])); for k=1:n c(k,k)=A(k,k); end; [q,dummy]=max(abs(diag(c))); for j=1:n %compute jth col of L l(j,j)=1; for s=1:j-1 l(j,s)=c(j,s)/d(s); end for i=j+1:n lc=0; for s=1:j-1 lc=lc+l(j,s)*c(i,s); end; c(i,j)=A(i,j)-lc; end theta(j)=0; if (j <=n) mc=0; for i=j+1:n if abs(c(i,j)) >mc mc= abs(c(i,j)) ; end theta(j)=mc; end end; tt=[abs(c(j,j)),(theta(j)/Bet)^2,delta]; d(j)=max(tt); if (j<n) for i=j+1:n c(i,i)=c(i,i)-c(i,j)^2/d(j); end; end; end
- mmf.math.linalg.cholesky.se99.air_modchol(A)[source]¶
This is based on the following c code from the AIR project:
/* Copyright 2000-2002 Roger P. Woods, M.D. */ /* Modified 7/19/02 */ /* * This implements the revised modified Cholesky factorization * algorithm described by Schnabel and Eskow. * * If A is not positive definite, it solves a nearby matrix that is. * * Schnabel RB, Eskow E, A revised modified Cholesky factorization * algorithm, Siam J Optim., 1999;9(4):1135-1148. * * Schnabel RB, Eskrow E. A new modified Cholesky factorization. Siam * J Sci Stat Comput, 1990;11(6):1136-1158 * * Note that for a sufficiently positive definite matrix, the method is * effectively Algorithm 4.2.4 in the 2nd edition of Golub and van Loan's * Matrix Computations * * Returns 0 if matrix was sufficiently positive definite * Returns 1 if some other nearby matrix had to be factored */ #include "AIR.h" #include <float.h> unsigned int AIR_modchol(double **a, const unsigned int n, unsigned int *ipvt, double *g) { double gamma=0.0; const double mu=0.1; const double tau=pow(DBL_EPSILON,1.0/3.0); const double tauhat=tau*tau; { unsigned int i; for(i=0;i<n;i++){ double temp=fabs(a[i][i]); if(temp>gamma) gamma=temp; } } { unsigned int j; /* Phase I, A is potentially positive definite */ for(j=0;j<n;j++){ unsigned int imax=j; { double min=a[j][j]; double max=min; { unsigned int i; for(i=j+1;i<n;i++){ double temp=a[i][i]; if(temp<min) min=temp; else if(temp>max){ max=temp; imax=i; } } } if(max<tauhat*gamma) break; if(min<-mu*max) break; } /* Pivot on maximum diagonal of remaining submatrix */ ipvt[j]=imax; if(imax!=j){ { double temp=a[j][j]; a[j][j]=a[imax][imax]; a[imax][imax]=temp; } { unsigned int i; for(i=0;i<j;i++){ double temp=a[j][i]; a[j][i]=a[imax][i]; a[imax][i]=temp; } } { unsigned int i; for(i=imax+1;i<n;i++){ double temp=a[i][imax]; a[i][imax]=a[i][j]; a[i][j]=temp; } } { unsigned int i; for(i=j+1;i<imax;i++){ double temp=a[i][j]; a[i][j]=a[imax][i]; a[imax][i]=temp; } } } { if(j<n-1){ double min=a[j+1][j+1]-a[j+1][j]*a[j+1][j]/a[j][j]; { unsigned int i; for(i=j+2;i<n;i++){ double temp=a[i][i]-a[i][j]*a[i][j]/a[j][j]; if(temp<min) min=temp; } } if(min<-mu*gamma) break; } /* Perform jth iteration of factorization */ a[j][j]=sqrt(a[j][j]); { unsigned int i; for(i=j+1;i<n;i++){ a[i][j]/=a[j][j]; { unsigned int k; for(k=j+1;k<=i;k++){ a[i][k]-=a[i][j]*a[k][j]; } } } } } } if(j==n) return 0; /* Phase two, a not positive definite */ if(j==n-1){ double delta=tau*(-a[j][j])/(1-tau); double temp=tauhat*gamma; ipvt[j]=j; if(temp>delta) delta=temp; a[j][j]=sqrt(delta); return 1; } else{ unsigned int k=j; double deltaprev=0.0; /* Calculate the lower Gerschgorin Bounds of a[k]*/ { unsigned int i; for(i=k;i<n;i++){ g[i]=a[i][i]; { unsigned int j1; for(j1=k;j1<i;j1++){ g[i]-=fabs(a[i][j1]); } } { unsigned int j1; for(j1=i+1;j1<n;j1++){ g[i]-=fabs(a[j1][i]); } } } } { /* Modified Cholesky decomposition */ unsigned int j1; for(j1=k;j1+2<n;j1++){ unsigned int imax=j1; double max=g[j1]; /* Pivot on maximum lower Gerschgorin bound estimate */ { unsigned int i; for(i=j1+1;i<n;i++){ if(g[i]>max){ max=g[i]; imax=i; } } } ipvt[j1]=imax; if(imax!=j1){ { double temp=a[j1][j1]; a[j1][j1]=a[imax][imax]; a[imax][imax]=temp; } { unsigned int i; for(i=0;i<j1;i++){ double temp=a[j1][i]; a[j1][i]=a[imax][i]; a[imax][i]=temp; } } { unsigned int i; for(i=imax+1;i<n;i++){ double temp=a[i][imax]; a[i][imax]=a[i][j1]; a[i][j1]=temp; } } { unsigned int i; for(i=j1+1;i<imax;i++){ double temp=a[i][j1]; a[i][j1]=a[imax][i]; a[imax][i]=temp; } } } /* Calculate E[j1][j1] and add to diagonal */ { double normj=0.0; double delta; { unsigned int i; for(i=j1+1;i<n;i++){ normj+=fabs(a[i][j1]); } } delta=normj; if(tauhat*gamma>delta){ delta=tauhat*gamma; } delta-=a[j1][j1]; if(delta<0.0) delta=0.0; if(delta<deltaprev) delta=deltaprev; if(delta>0.0){ a[j1][j1]+=delta; deltaprev=delta; } /* Update Gerschgorin bound estimates */ if(a[j1][j1]!=normj){ double temp=1-normj/a[j1][j1]; { unsigned int i; for(i=j1+1;i<n;i++){ g[i]+=fabs(a[i][j1])*temp; } } } } /* Perform j1th iteration of factorization */ a[j1][j1]=sqrt(a[j1][j1]); { unsigned int i; for(i=j1+1;i<n;i++){ a[i][j1]/=a[j1][j1]; { unsigned int k1; for(k1=j1+1;k1<=i;k1++){ a[i][k1]-=a[i][j1]*a[k1][j1]; } } } } } } /* Final 2x2 submatrix */ { double lambdahi=a[n-2][n-2]-a[n-1][n-1]; double lambdalo; ipvt[n-2]=n-2; ipvt[n-1]=n-1; lambdahi=lambdahi*lambdahi; lambdahi+=4.0*a[n-1][n-2]*a[n-1][n-2]; lambdahi=sqrt(lambdahi); lambdalo=-lambdahi; lambdahi+=(a[n-2][n-2]+a[n-1][n-1]); lambdalo+=(a[n-2][n-2]+a[n-1][n-1]); lambdahi/=2.0; lambdalo/=2.0; { double delta=tau*(lambdahi-lambdalo)/(1-tau); if(tauhat*gamma>delta) delta=tauhat*gamma; delta-=lambdalo; if(delta<0.0) delta=0.0; if(delta<deltaprev) delta=deltaprev; if(delta>0.0){ a[n-2][n-2]+=delta; a[n-1][n-1]+=delta; deltaprev=delta; } a[n-2][n-2]=sqrt(a[n-2][n-2]); a[n-1][n-2]/=a[n-2][n-2]; a[n-1][n-1]=sqrt(a[n-1][n-1]-a[n-1][n-2]*a[n-1][n-2]); } } return 1; } } }