Background
The data set:
A long time ago, a study collected paired estimates of the EIR and the PR [1]; some of this was a thesis [FanelloC2000RelationshipEntomological?].
Then Simon worked on it [2]
We took a mechanistic approach [3,4]
Then we redid it once [5]
Then we redid it again [6]
- not me but also useful [7]
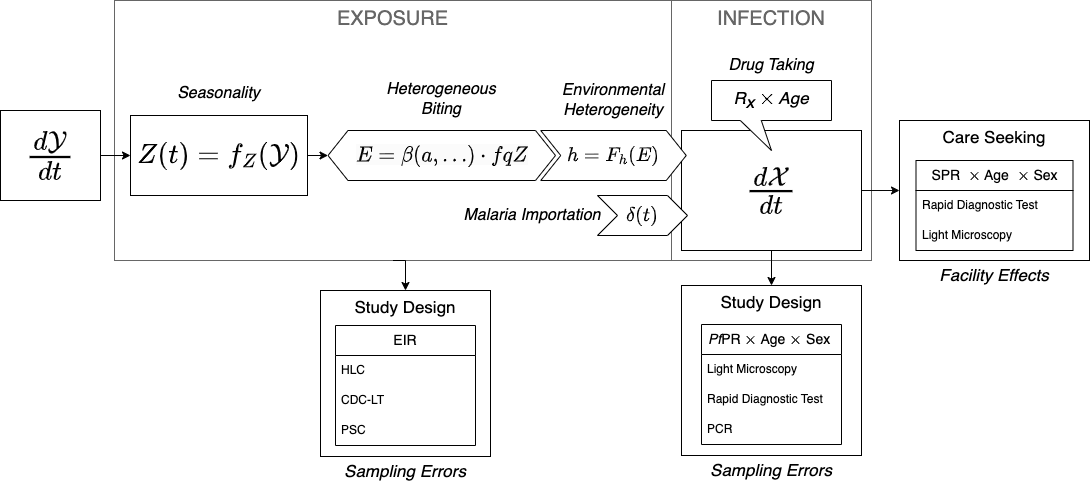
Variability
Among the local factors affecting the relationship between the average annual EIR and the average annual PR are:
Drug Taking
Seasonality – the relationship between the average annual EIR and the average annual PR is lower, but the orbits all like to the left of the average curve.
Spatial Heterogeneity – mosquito populations are highly spatially heterogeneous; this gets averaged out by human mobility patterns
Heterogeneous Biting – some people get more bites on average than others; we handle this with biting weights
Environmental Heterogeneity – exposure rates are highly variabile even with a population stratum; variance around the mean gives negative binomial exposure rates
Travel Malaria
Measurement Errors
Differences in the PfPR by study design: age, sex, location and time of year
Differences in the PfPR diagnostic method
Differences in the mosquito sampling strategy
References
1.
Beier JC, Killeen GF, Githure JI. Short report: Entomologic inoculation rates and
Plasmodium falciparum malaria prevalence in
Africa. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 1999;61: 109–113. doi:
10.4269/ajtmh.1999.61.109
2.
Hay SI, Guerra CA, Tatem AJ, Atkinson PM, Snow RW. Urbanization, malaria transmission and disease burden in
Africa. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005;3: 81–90. doi:
10.1038/nrmicro1069
3.
Smith DL, Dushoff J, Snow RW, Hay SI. The entomological inoculation rate and
Plasmodium falciparum infection in
African children. Nature. 2005;438: 492–495. doi:
10.1038/nature04024
4.
Smith DL, McKenzie FE, Snow RW, Hay SI. Revisiting the basic reproductive number for malaria and its implications for malaria control. PLoS Biol. 2007;5: e42. doi:
10.1371/journal.pbio.0050042
5.
Gething PW, Patil AP, Smith DL, Guerra CA, Elyazar IRF, Johnston GL, et al. A new world malaria map:
Plasmodium falciparum endemicity in 2010. Malar J. 2011;10: 378. doi:
10.1186/1475-2875-10-378
6.
Penny MA, Maire N, Bever CA, Pemberton-Ross P, Briët OJT, Smith DL, et al. Distribution of malaria exposure in endemic countries in
Africa considering country levels of effective treatment. Malar J. 2015;14: 384. doi:
10.1186/s12936-015-0864-3
7.
Kelly-Hope LA, McKenzie FE. The multiplicity of malaria transmission: A review of entomological inoculation rate measurements and methods across sub-
Saharan Africa. Malar J. 2009;8: 19. doi:
10.1186/1475-2875-8-19
