The first model we considered was rather basic. We assumed constant temperature and pressure.

We then simply considered the steady-state relationship between the various reaction rate equations as we varied temperature and reactant concentration. The rate equations for the three reactions are:
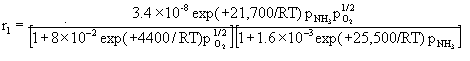
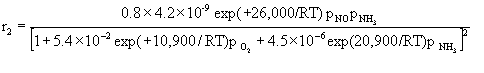
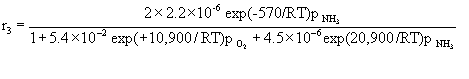
The governing equation for the change in reactant and product concentration in terms of their molar flow rates is:
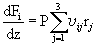
This equation yields a set of six coupled ordinary differential equations (ODEs) that must be solved simutaneously. As the initial concentrations are known, this is an initial value problem. We solved this set of ODEs in Matlab using ODE45, which employs a 4th order Runge-Kutta numerical method. Our results showed that the yield of NO increased with temperature. Click below to see how temperature and concentration change along the microreactor.
|
|
|
| Return to Optimization | Go on to Model 2 |