|
|
Economics
301
|
|
|
Last updated: January 25, 2000 Note: These notes are preliminary and incomplete and they are not guaranteed to be free of errors. Please let me know if you find typos or other errors. The Worker's Labor Supply DecisionPreviously, we took the supply of labor as given. That is, we assumed that firms could hire as many workers at the prevailing real wage. Realistically, we have to recognize that workers make a choice regarding how much they work and this labor supply decision interacts with firms' demand for labor to set the real wage and employment level in the economy. The labor supply decision involves the following:
Income and Substitution EffectsConsider how an increase in the current real wage affects a worker's labor supply. From microeconomics we recognize that there are two offsetting effects:
Which effect wins out when w increases is ambiguous since it depends on personal preferences towards current and future consumption and leisure. Empirical evidence on US aggregate labor supplyIn the book Labor Supply by Mark Killingsworth, it is reported that, for US data, temporary increases in real wages, w, tend to increase labor supply, NS, and that permanent increases in w tend to decrease NS. This implies that the substitution effect is stronger for temporary increases in w and that the income effect is stronger for permanent effects. Factors that Influence Labor Supply
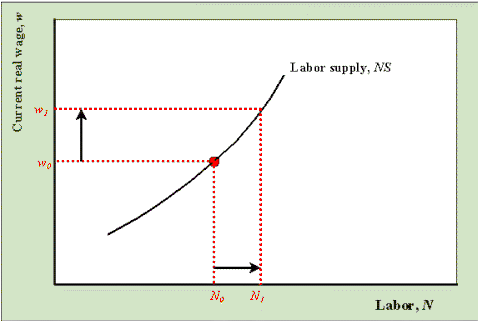
Aggregate Labor supplyAggregate labor supply is simply the sum of everyone's individual labor supplies. Graphical Description of Labor SupplyIncrease in the current real wage
An increase in the current real wage, holding everything else fixed, increases labor supply, NS, and this is represented as a movement along the curve. Increase in the expected future real wage
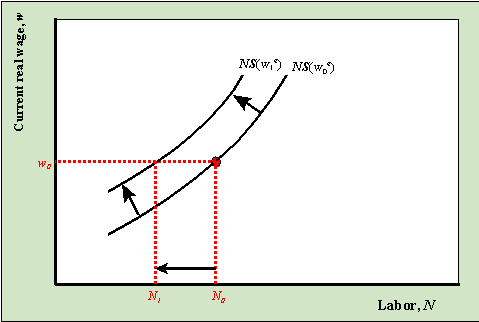
An increase in the expected future real wage, holding everything else fixed, decreases labor supply which is represented as a leftward shift of the NS curve. Increase in wealth
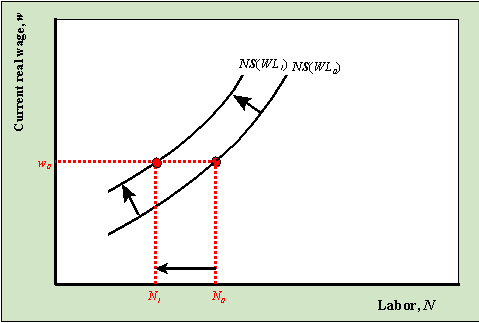
An increase in wealth, holding everything else fixed, decreases labor supply which is represented as a leftward shift of the NS curve.
|
|