 | How the Nervous
System Interacts with Other Body Systems |  |
| All of the systems within the body interact with one another to keep an organism healthy. Although each system has specific functions, they are all interconnected and dependent on one another. The nervous system controls various organs of the body directly. The brain also receives information from many organs of the body and adjusts signals to these organs to maintain proper functioning. | ||
| SYSTEM | FUNCTION | ASSOCIATED ORGANS | INTERACTION WITH THE NERVOUS SYSTEM |
| Skeletal
System
|
The skeletal system makes up the framework of the body and allows us to move when our muscles contract. It stores minerals (e.g. calcium, phosphorous) and releases them into the body when they are needed. The skeletal system also protects internal organs and produces blood cells. | Bones (e.g., skull, vertebrae) |
|
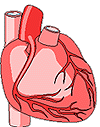
| Cardiovascular System
|
The cardiovascular system delivers oxygen, hormones, nutrients and white blood cells around the body by pumping blood, and it removes waste products. | Heart, blood vessels |
|
| Muscular
System
|
Different types of muscles enable motion, generate heat to maintain body temperature, move food through digestive tract and contract the heart. | Muscles (smooth, skeletal and cardiac muscles) |
|
| Endocrine
System
|
The endocrine system secretes hormones into blood and other body fluids. These chemicals are important for metabolism, growth, water and mineral balance, and the response to stress. | Pineal body, pituitary gland, hypothalamus, thyroid, parathyroid, heart, adrenal gland, kidney, pancreas, stomach, intestines, ovary |
|
| Lymphatic
System
|
The lymphatic system protects the body from infection. | Adenoid, tonsils, thymus, lymph nodes, spleen |
|
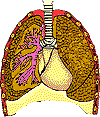
| Respiratory System
|
The respiratory system supplies oxygen to the blood and removes carbon dioxide. | Lungs, larynx, pharynx, trachea, bronchi |
|
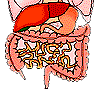
| Digestive
System
|
The digestive system stores and digests foods, transfers nutrients to the body, eliminates waste and absorbs water. | Stomach, esophagus, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, intestines |
|
| Reproductive System
|
The reproductive system is responsible for producing new life. | Testes, vas deferens, prostate gland, ovary, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix |
|
| Urinary
System
|
The urinary system eliminates waste products and maintains water balance and chemical balance. | Bladder, urethra, kidney |
|
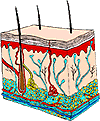
| Integumentary System
|
The integumentary system reduces water loss, contains receptors that respond to touch, regulates body temperature, and protects the inside of the body from damage. | Skin, hair |
|
| BACK TO: | Exploring the Nervous System | Table of Contents |
![[email]](./gif/menue.gif) Send |
 Get Newsletter |
 Search Pages |
 Donate to Neuroscience for Kids |