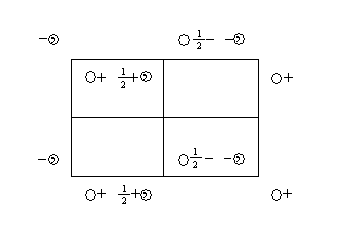
Equivalent Positions
The other figure on this space group page shows the location of the equivalent positions in the cell. If you start with an object in the cell (represented by the open circle in the upper lefthand corner of the cell), and operate on it with the symmetry elements, you generate the other objects. The objects related by symmetry within the unit cell take up what are called equivalent positions.

For this space group, there are four equivalent positions, two in one hand and two in the other.
The coordinates of the equivalent positions are listed below the figures.
For
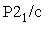 , there are four general positions with site symmetry 1. The coordinates for them are:
, there are four general positions with site symmetry 1. The coordinates for them are:

So if there's an atom at a general position, there are three others in equivalent positions in the cell.
The positions below the general ones are called special positions. They're special because they're locations with special symmetry properties. In this space group, the locations of the inversion centers are special. If an atom is located on a center, the inversion operation transforms the atom onto itself, and the number of equivalent sites is reduced to two. There are four such sets of paired centers and they're listed under the general positions.
 back to index
back to index
 next topic
next topic
 previous topic
previous topic
copyright © Ron Stenkamp stenkamp@u.washington.edu Most recent update 5/1/03