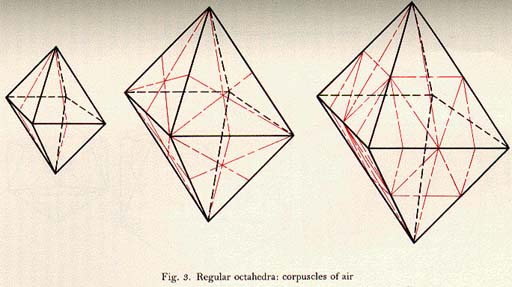
Each particle, or corpuscle, of air is a regular octohedron (8-sided geometrical solid). This is what air particles look like, according to Plato’s description in the Timaeus. In the center is the air-particle Plato describes at 55a, with 6 scalene triangles making up each equilateral face of the octohedron. On the left is a simpler “isotope” with 2 scalene triangles per face; on the right is a more complex “isotope” with 8 scalene triangles per face.

Image taken from Friedländer, Plato, vol. 1, An Introduction.
![]() Return to
Timaeus lecture.
Return to
Timaeus lecture.
![]() Return to the PHIL 320 Home Page
Return to the PHIL 320 Home Page