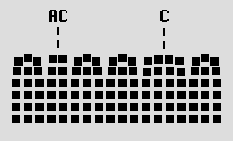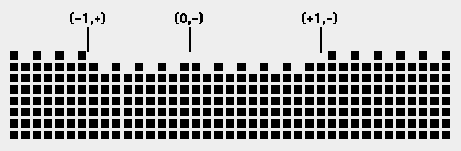COMPETITION BETWEEN SURFACE RECONSTRUCTION AND (PRE)-ROUGHENING TRANSITIONS
Roughening Induced Deconstruction in (100) Facets of CsCl Type Crystals,
Douglas Davidson and Marcel den Nijs,
Phys.Rev. E 55, 1331 (1997).
Preroughening Induced Deconstruction in Si and Ge (001) Type Surfaces,
Marcel den Nijs, J.Phys. A 30, 397 (1997).
Roughening, Preroughening, and Reconstruction Transitions in Crystal Surfaces,
Marcel den Nijs, chapter 4 in
The Chemical Physics of Solid Surfaces and Heterogeneous Catalysis, Vol.7
edited by D. King, Elsevier (Amsterdam, 1994).
Competition between Surface Roughening and Deconstruction in (110)
facets of FCC Crystals,
Marcel den Nijs,
Phys.Rev. B 46, 10386 (1992).
|
Surface reconstructions can be divided into two groups:
displacement and misplacement reconstructions.
Compared to the unreconstructed configuration,
particles on the surface are moved only locally
or are transported away completely.
Misplacement reconstructed surfaces have typically a different average surface height than
their unreconstructed counter parts. The top layer(s) can be interpreted as only
partially completed and have long range positional order.
|
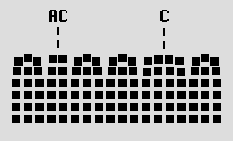
displacement reconstruction with topological defects
|
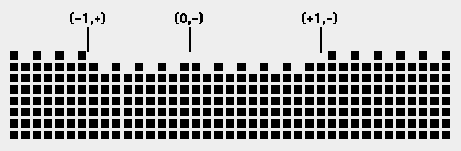
misplacement reconstruction with topological defects
Above the deconstruction phase transition temperature, misplacement reconstructed
surfaces become disordered flat (DOF).
The top layer(s) are still only partially completed but now lack positional order.
The DOF surface structure is not considered rough. Surface roughness is a large scale
phenomena where the surface interface width measured over a length scale L diverges
with L. From a surface roughening perspective, a DOF phase is a step liquid with long range
topological up-down order.
A preroughening transition
is a phase transition from an ordered flat phase into a DOF phase.
Surface roughening and reconstruction transitions can compete.
Roughness can be compatible or incompatible with
the reconstruction depending on topological details of the crystal structure and
the type of reconstruction.
For example, the roughening and reconstruction degrees of freedom decouple
in missing row reconstructed simple cubic (110) facets; such that
a so-called reconstructed rough phase is possible.
The same degrees of freedom couple strongly in
FCC (110) facets like Au(110) and Pt(110) ,
such that surface roughening can not take place before the reconstruction order parameter vanishes.
Roughening induces a simultaneous deconstruction transition if the surface does not deconstruct
before it roughens.
Another example is the Si(001) type 1x2 reconstruction;
(pre-)roughening must induce a simultaneous deconstruction transition.
|
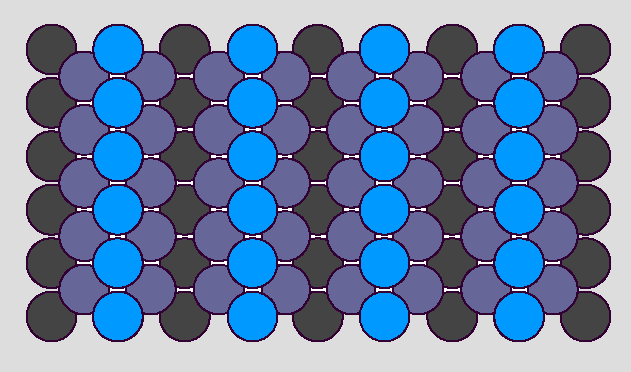
top view of a FCC(110) missing row reconstruction
home page of Marcel den Nijs