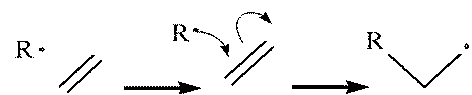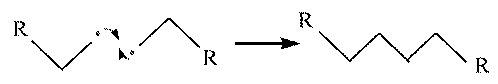Polymerization
Polyethylene develops
through a normal polymerization reaction. After initiated,
thousand of individual ethylene molecules link together. The
prosess occurs in the following steps:
- Initiation.
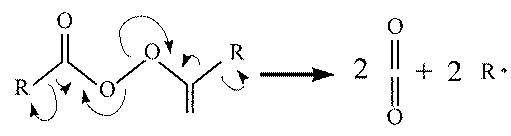
An organic peroxide initiates the reaction. The peroxide
breaks down into two organic radicals (R*) and two
neutral carbon dioxide moleculses.
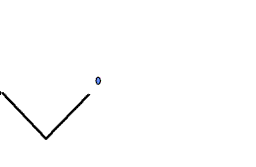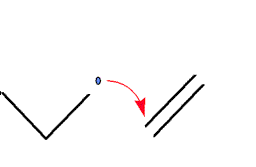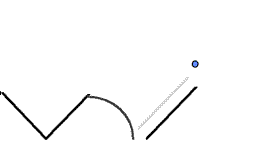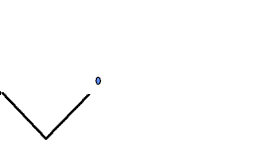
- Propogation.
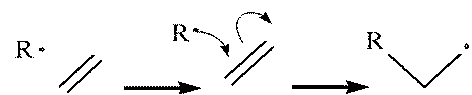
The radical attacks an ethylene molecule, attaching
itself to the molecule and leaving the molecule as a
whole as a radical. This process continues until a
termination finally occurs.
- Termination.
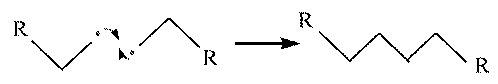
The reaction terminates when a radical attacks another
radical, terminating the propagation step for both of
them.
If you're interested in
examining a calculations on this process, checkout a homework
problem.
To find out more about the
chemicals that help control this reaction, read on in the catalyst section.