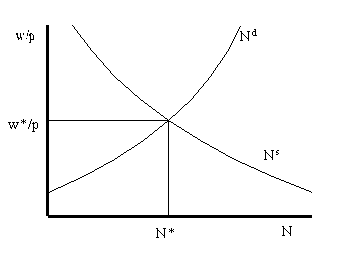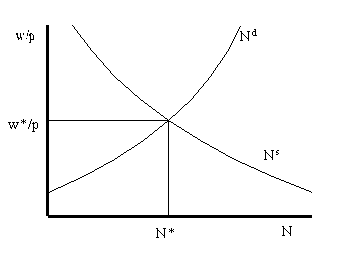Unemployment definitions and statistics
Reading: AB, chapter 3, section 4.
Types of Unemployment
- Frictional Unemployment: unemployment caused by workers searching for jobs and firms
searching for workers.
- Structural Unemployment: long-term chronic unemployment that exists when the economy is
not in a recession. The main causes of structural unemployment are: (1) the number of low
skilled workers exceeds the number of low skilled jobs (dual labor market idea); (2) some
sectors of the economy are contracting while others are expanding and the contracting
industries create unemployment.
- Natural Rate of Unemployment: unemployment rate consistent with full employment =
frictional rate + structural rate = u*. Currently the natural rate is estimated to be somewhere
between 5.5% and 6.5%. However, it is not estimated very precisely. (Note: equilibrium
values are denoted with a superscript "*" instead of an overbar since I can't get overbars to
print in HTML.)
- Cyclical Unemployment: actual rate of unemployment - natural rate of unemployment = u - u*.
The cyclical rate of unemployment is the unemployment created by recessions and booms.
During recessions, u - u* > 0; during booms, u - u* < 0.
- Actual Unemployment Rate: natural rate + cyclical rate = u = u* + (u - u*).
- NAIRU: non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment = rate of inflation consistent with
stable prices/inflation = natural rate of unemployment. The NAIRU and the natural rate are the
same thing. As we shall see, the natural rate of unemployment (NAIRU) is the rate of
unemployment that exists when inflation is neither increasing nor decreasing. When the
economy is booming, cyclical unemployment is positive and inflation tends to accelerate; when
the economy is in recession, cyclical unemployment is negative and inflation tends to
decelerate.
Graphical illustration of u*
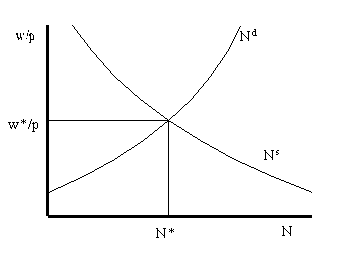
The natural rate of unemployment, u*, is the unemployment rate that occurs when the labor
market is in equilibrium; i.e. when employment is N*.
Unemployment Statistics
- Labor force (LF): number of employed individuals (E) + number of unemployed individuals
seeking work (U).
- Not in the labor force (NLF): those individuals neither employed nor unemployed and not
seeking work.
- Adult population: LF + NLF.
- Unemployment rate: u = U/(E + U). Note that the unemployment rate changes whenever U or
E changes.
[insert pie chart of unemployment statistics here]
Counter intuitive facts about unemployment
- Most spells of unemployment (i.e., time spend unemployed) are short - about 2 months
- Most people who are unemployed on a given date are experiencing long unemployment spells
(i.e., have been unemployed for a long time - about 1 year).
[Next Slide] [Contents for Lecture 5] [301 Homepage]
Last Updated July 8, 1996 by Eric Zivot