 | Cranial Nerves |  |
| The cranial nerves are 12 pairs of nerves that can be seen on the ventral (bottom) surface of the brain. Some of these nerves bring information from the sense organs to the brain; other cranial nerves control muscles; other cranial nerves are connected to glands or internal organs such as the heart and lungs. |
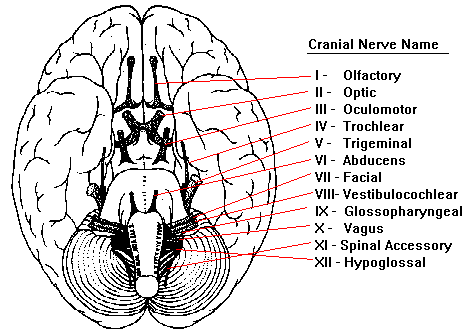 |
| Cranial Nerves | |||
| Number | Name | Function | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Olfactory Nerve | Smell | 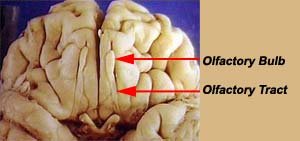 |
| II | Optic Nerve | Vision | 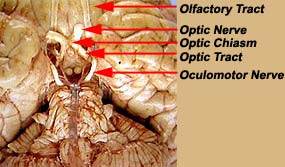 |
| III | Oculomotor Nerve | Eye movement; pupil constriction | 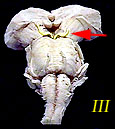 |
| IV | Trochlear Nerve | Eye movement | 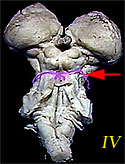 |
| V | Trigeminal Nerve | Somatosensory information (touch, pain) from the face and head; muscles for chewing. | 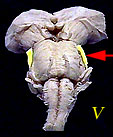 |
| VI | Abducens Nerve | Eye movement | 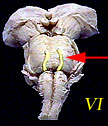 |
| VII | Facial Nerve | Taste (anterior 2/3 of tongue); somatosensory information from ear; controls muscles used in facial expression. | 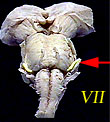 |
| VIII | Vestibulocochlear Nerve | Hearing; balance | 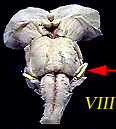 |
| IX | Glossopharyngeal Nerve | Taste (posterior 1/3 of tongue); Somatosensory information from tongue, tonsil, pharynx; controls some muscles used in swallowing. | 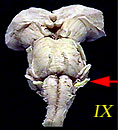 |
| X | Vagus Nerve | Sensory, motor and autonomic functions of viscera (glands, digestion, heart rate) | 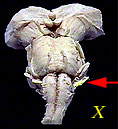 |
| XI | Spinal Accessory Nerve | Controls muscles used in head movement. | 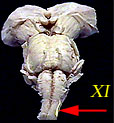 |
| XII | Hypoglossal Nerve | Controls muscles of tongue | 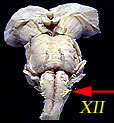 |
| Note: the olfactory "nerve" is composed of the rootlets of
olfactory hair cells in the nasal mucosa and is not visible on the ventral
surface of the brain. The rootlets end in the olfactory bulb. The
olfactory tract contains nerve fibers projecting out of the olfactory bulb
to the brain. The images in this table have been adapted from those in the Slice of Life project. | |||
 Hear IT! | Olfactory | Optic | Oculomotor | Trochlear |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trigeminal | Abducens | Facial | Vestibulocochlear | |
| Glossopharyngeal | Vagus | Spinal Accessory | Hypoglossal |
|
Can't remember the names of the cranial nerves? Here is a handy-dandy
mnemonic for you: On Old Olympus Towering Top A Famous Vocal German Viewed Some Hops. The bold letters stand for: olfactory, optic, oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal, abducens, facial, vestibulocochlear, glossopharyngeal, vagus, spinal accessory, hypoglossal.
|
Test Your Cranial NervesYou will need to get a partner to help...both of you can serve as the experimenter (tester) and the subject. Record your observations of what your partner does and says.

Check the pupillary response (oculomotor nerve): look at the diameter of your partner's eyes in dim light and also in bright light. Check for differences in the sizes of the right and left pupils.
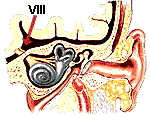 Vestibulocochlear
Nerve (VIII) Vestibulocochlear
Nerve (VIII)
|
Try it! | Do you like interactive word search puzzles?
Make sure your browser is "java-enabled" and try this one:
|
| BACK TO: | Exploring the Nervous System | Table of Contents |
![[email]](./gif/menue.gif) Send E-mail |
 Get Newsletter |
 Search Pages |
 Donate to Neuroscience for Kids |
 To test the sensory part of the
trigeminal nerve, lightly touch various parts of your partner's face with
piece of cotton or a blunt object. Be careful not to touch your partner's
eyes. Although much of the mouth and teeth are innervated by the
trigeminal nerve, don't put anything into your subject's mouth.
To test the sensory part of the
trigeminal nerve, lightly touch various parts of your partner's face with
piece of cotton or a blunt object. Be careful not to touch your partner's
eyes. Although much of the mouth and teeth are innervated by the
trigeminal nerve, don't put anything into your subject's mouth.