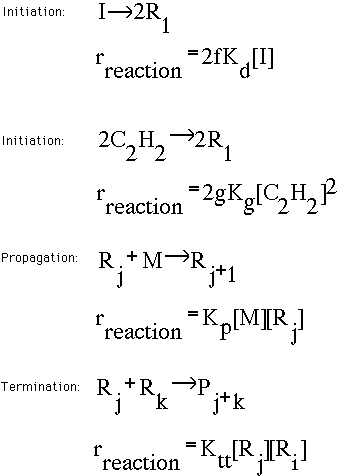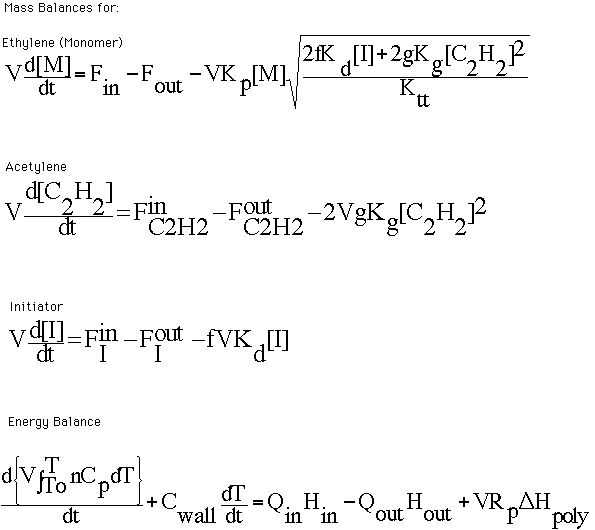
Polymerization Reaction Kinetics
The free radical reaction takes place in three major steps, Initiation,
Propagation, and Termination. The initiation is the first step that forms
the free radical from the monomer, or existing polymer chains, that grow
even larger. The initiation step basically forms free radicals that react
with other neighboring molecules that have the propensity to form radicals
too. The radicals are formed and the propagation step begins. Here, the
radicals continue to collide and form other radicals, and hence initialize
a chain reaction of radical formation. The rate of propagation is
determined by the concentration of free radicals in the reactor. As
radicals collide with one another, the radicals form longer chain
molecules. This is essentially what chain termination involves. Below
are a series of reaction mechanisms that characterize the free-radical
polymerization process.
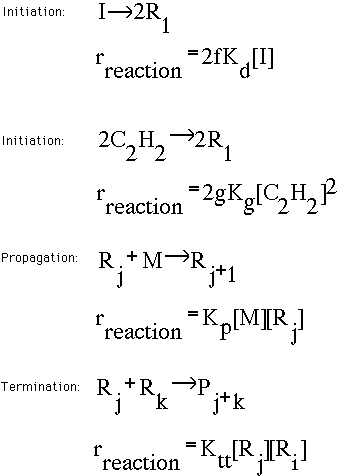
|
|
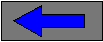
The rate laws are then used to derive the mass
and energy balances that describe the dynamics of the reaction process.
The mass balances shown are derived for the ethylene monomer, acetylene
and the initiator.
|
|