Other Structural Studies
Section I 4.2 Mammalian Phosphodiesterase GAF domains
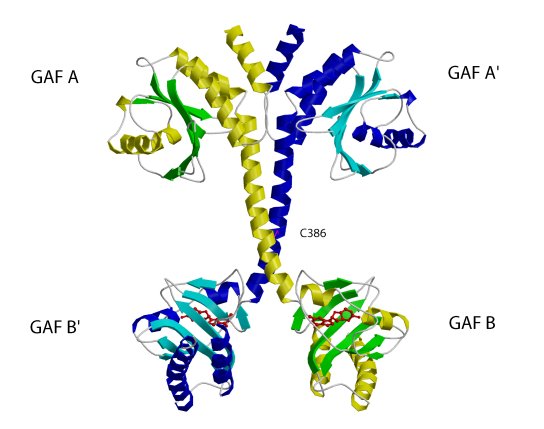
The structure of the regulatory segment of mouse . Each PDE2A
subunit contains a GAF A and a GAF B domain. The GAF A domain and seven turns
of the connecting helices form a dimer interface. The two GAF B domains are
far apart and contain the cGMP-binding sites. View showing the dimer interface
of the regulatory segment.
(Sergio Martinez)
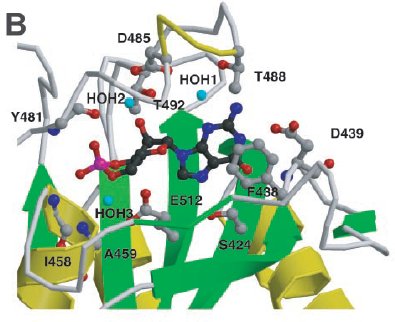
cGMP binding by PDE2A. Close-up view of the cGMP-binding site
in GAF B. Shown are six side chains that make hydrogen bonds to the cGMP,
one that stacks with the guanine ring, and two that make backbone amide contacts.
Helix α4 and strand β3' are depicted as coils for visibility of
the cGMP.
(Sergio Martinez)
Section I 4.3 Heat Shock protein Hsp31
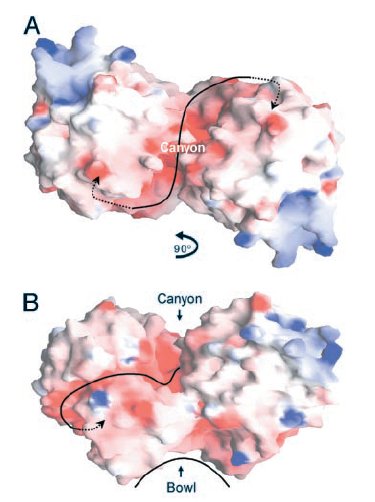
Two views of the electrostatic potential of the EcHsp31 dimer. Electrostatic surfaces are colored between -10 kT (red) and +10kT (blue). Canyon and bowl are labeled.
(A)The negative groove connecting the putative triads is shown by a black line, with negative groove connecting the putative triads is shown by a black line, with arrows pointing to triad(s). View down the crystallographic twofold axis.
(B) View perpendicular to the twofold axis, looking through
the canyon of the A domains.
(Paulene Quigley)
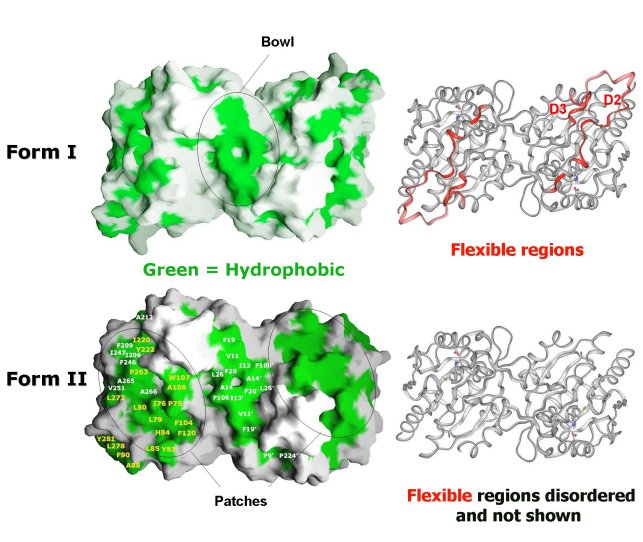
Comparison of Form I EcHsp31 (top) and Form II EcHsp31 dimer
(bottom). Molecular surface of dimers shown with hydrophobic patches in green.
Ribbon representation of dimers are shown on the right in the same
orientation. Red ribbons in Form I EcHsp31 highlight regions that are disordered
in the Form II EcHsp31. Note that the differences (red) between Form I EcHsp31
and Form II EcHsp31 dimer result in the exposure of more hydrophobic regions
(green patches) in Form II EcHsp31. These areas are circled in black.
(Paulene Quigley)
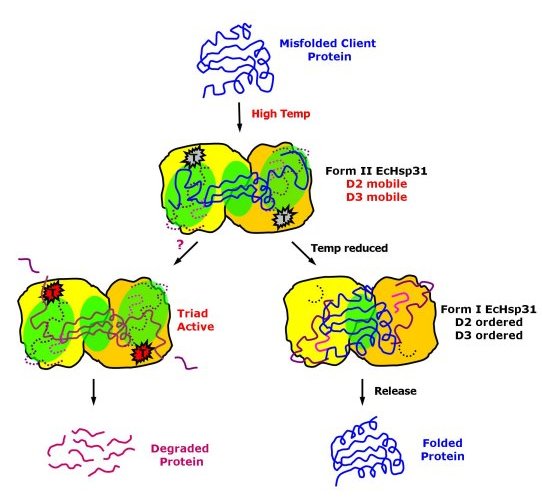
Possible mechanism of chaperone activity of EcHsp31 and possible
hydrolytic functions at high temperatures.
(Paulene Quigley)
For more information about this subject, please see the Research Summary text, Part I Section 4.