Lab 3
This lab will be mostly focused on constructing loops inside of loops
Contents
Exercise 1: Summing matrix entries
The commands
n = 10; A = rand(n);
generate an  matrix with randomly chosen elements. This is an easy way to generate a matrix to test an algorithm. Write code to generate A and then loop through all its elements to sum all the elements. Let a variable
matrix with randomly chosen elements. This is an easy way to generate a matrix to test an algorithm. Write code to generate A and then loop through all its elements to sum all the elements. Let a variable
SUM
be the total sum of all the entries. For 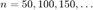 plot
plot
SUM/(n^2/2)
against  . What do you notice?
. What do you notice?
Exercise 2: Vectorizing
MATLAB® is much more efficient when you add two vectors instead of adding a large number of scalars. Thisiis sometimes called vectorizing: allowing your code to run purely with vector operations. For example,
A(1,:) + A(2,:)
will add the first two rows of  . Perform the same steps as in the previous exercise by
. Perform the same steps as in the previous exercise by
- First, sum all the rows of
 , constructing a vector.
, constructing a vector. - Secton, sum all the elements of the vector.
Use the
tic/toc
commands to examine the speed difference.
Exercise 3: Triangular matrices
Define the matrix  as in Exercise 1. Write code that zeros out entries to make
as in Exercise 1. Write code that zeros out entries to make  an upper-triangular matrix. Do the same to make
an upper-triangular matrix. Do the same to make  a lower-triangular matrix.
a lower-triangular matrix.