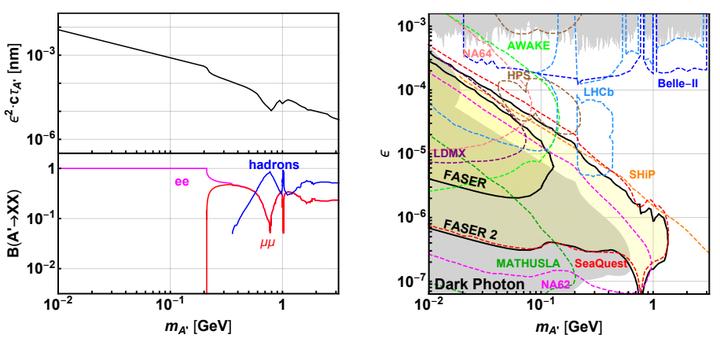
 Benchmark Model V1. The dark photon decay length (top left panel), its branching fractions into hadronic and leptonic final states (bottom left panel) and FASER’s reach (right panel). In the right panel, the gray-shaded regions are excluded by current bounds, and the projected future sensitivities of other experiments are shown as colored contours. See the text for details.
Benchmark Model V1. The dark photon decay length (top left panel), its branching fractions into hadronic and leptonic final states (bottom left panel) and FASER’s reach (right panel). In the right panel, the gray-shaded regions are excluded by current bounds, and the projected future sensitivities of other experiments are shown as colored contours. See the text for details.
Abstract
The ForwArd Search ExpeRiment (FASER) is an approved experiment dedicated to searching for light, extremely weakly interacting particles at the LHC. Such particles may be produced in the LHC’s high-energy collisions and travel long distances through concrete and rock without interacting. They may then decay to visible particles in FASER, which is placed 480 m downstream of the ATLAS interaction point. In this work we briefly describe the FASER detector layout and the status of potential backgrounds. We then present the sensitivity reach for FASER for a large number of long-lived particle models, updating previous results to a uniform set of detector assumptions, and analyzing new models. In particular, we consider all of the renormalizable portal interactions, leading to dark photons, dark Higgs bosons, and heavy neutral leptons; light $B − L$ and $L_i − L_j$ gauge bosons; axionlike particles that are coupled dominantly to photons, fermions, and gluons through nonrenormalizable operators; and pseudoscalars with Yukawa-like couplings. We find that FASER and its follow-up, FASER 2, have a full physics program, with discovery sensitivity in all of these models and potentially far-reaching implications for particle physics and cosmology.
Supplementary notes can be added here, including code and math.