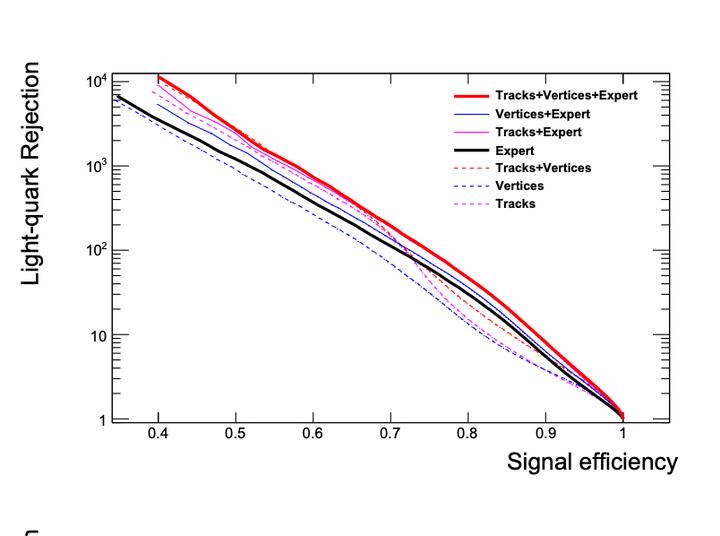
 Signal efficiency versus background rejection (inverse of efficiency) for deep networks trained on track-level, vertex-level or expert-level features.
Signal efficiency versus background rejection (inverse of efficiency) for deep networks trained on track-level, vertex-level or expert-level features.
Abstract
Classification of jets as originating from light-flavor or heavy-flavor quarks is an important task for inferring the nature of particles produced in high-energy collisions. The large and variable dimensionality of the data provided by the tracking detectors makes this task difficult. The current state-of-the-art tools require expert data reduction to convert the data into a fixed low-dimensional form that can be effectively managed by shallow classifiers. We study the application of deep networks to this task, attempting classification at several levels of data, starting from a raw list of tracks. We find that the highest-level lowest-dimensionality expert information sacrifices information needed for classification, that the performance of current state-of-the-art taggers can be matched or slightly exceeded by deep-network-based taggers using only track and vertex information, that classification using only lowest-level highest-dimensionality tracking information remains a difficult task for deep networks, and that adding lower-level track and vertex information to the classifiers provides a significant boost in performance compared to the state of the art.
Supplementary notes can be added here, including code and math.