Exam 1 Study Guide
Disclaimer: This is intended as a study aid. It is not a complete description of everything discussed in class, nor an exhaustive list of information that might be tested on an exam. This is not intended to be a substitute for class attendance.
LECTURE OUTLINES
What is psychology?
I. Goals of psychology
to observe, explain, predict behavior
II. Areas within psychology
A. basic research
1. biopsychology
2. developmental psych
3. social psych
4. cognitive psych
5. personality psych
B. applied psychology
1. clinical and counseling
2. industrial/organizational
Psychology as a science
I. Scientific Method (theory, hypothesis, observation)
II. Experimental method of observation
A. independent and dependent variables
B. confounding variables, and how to control them
1. confounding placebo effect
2. confounding subject varaiables
C. examples of experiments were discussed in class and illustrated in a film
III. Non-experimental method of observation
A. correlation -- allows predictions but does not permit claims about cause-and-effect
Biopsychology (Neuroscience)
I. Basic divisions of the nervous system
A. CNS - PNS
B. somatic - autonomic
C. sympathetic - parasympathetic
II. Microscopic view of the brain -- neurons
A. structure and function of neurons
1. dendrites -- collect information
2. cell body -- integrates info, makes decision about whether to send signal to other neurons
3. axon -- transmits signal to other neurons
B. How a neuron processes information
1. electrical mechanism (flow of charged ions)
2. concepts of resting potential, thresold potential, excitatory and inhibitory signals, action potential
C. How a neuron communicates with other neurons: the synapse
1. elements of a synapse (presynaptic neuron, postsynaptic neuron, synaptic gap)
2. presynaptic events
3. postsynaptic events
4. examples of neurotransmitters
5. drugs and the synapse
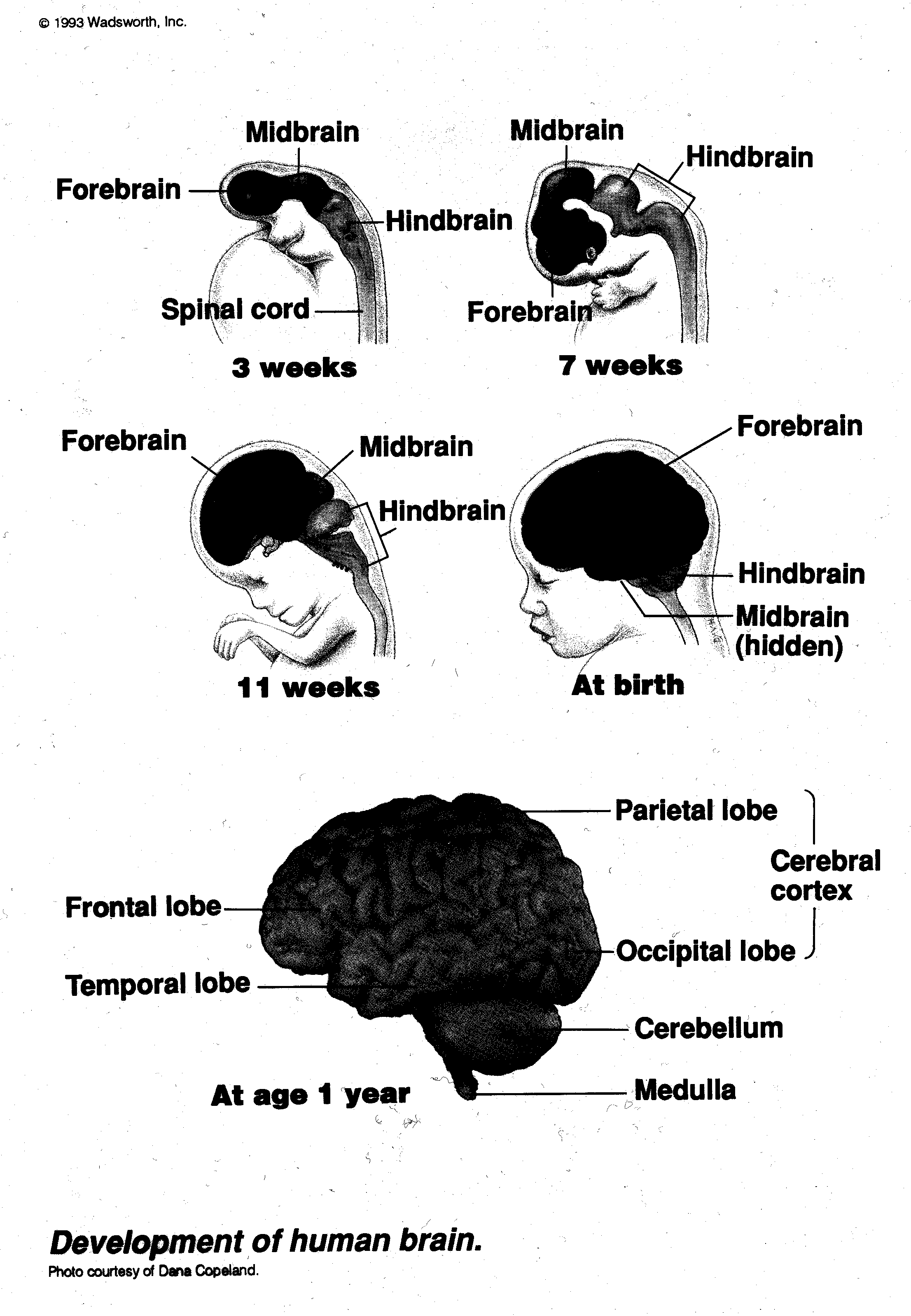
III. Macroscopic view of the brain
A. location and function of brain structures (e.g., medulla, cerebellum, colliculi, etc)
B. cerebral cortex
1. major fissures, lobes
2. functional divisions of cortex (sensory, motor, association)
3. hemispheric lateralization of function; split-brain patients
Developmental Psychology
I. How competent is the newborn?
A. types of behaviors a newborn is capable of
II. General developmental issues
A. Types of change
B. Two important developmental issues
1. nature vs nurture
2. continuous change vs change in stages
III. Prenatal-environmental influences
A. e.g., fetal alcohol syndrome
IV. Cognitive Development
A. Piaget's theory
1. assumptions
2. basic concepts
3. stages of development
4. criticisms/limitations
V. Social Development
A. Infant-caregiver attachments
1. Why do infants become attached to caregivers?
2.What determines the quality of attachment?
3. What long-term effects does quality of attachment have?
VI. Aging
A. How bad is old age?
B. Alzheimer's disease
HINTS FOR STUDYING
There will almost definitely be questions about the following things (and on other topics too):
I. Psych as a science
experimental method
- independent variables, dependent variables, confounding variables, control conditions
correlation
- what it can and cannot tell you; contrast with experiments
statistics
- mean, median, mode; central tendency
II. Behavioral Neuroscience
basic divisions of nervous system
neurons
- parts of neuron; synapses; action potentials; ions; neurotransmitters; synapse; re-uptake; drugs
macroscopic view of brain
- brain structures and their functions, including hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain structures; especially cortex
III. Development
capabilities of newborn
domains of change
biological development
- fetal alcohol syndrome
- Rosenzwieg study with rats
cognitive development
- Piaget's theory; modern-day critiques of Piaget's theory
aging
- how bad is old age?
- Alzheimer's disease
LECTURE TRANSPARENCIES
On this page are transparencies shown in class that are not provided in the text.
Brain Development (basic divisions of hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain)
Brain structures as seen from the interior of the left hemisphere