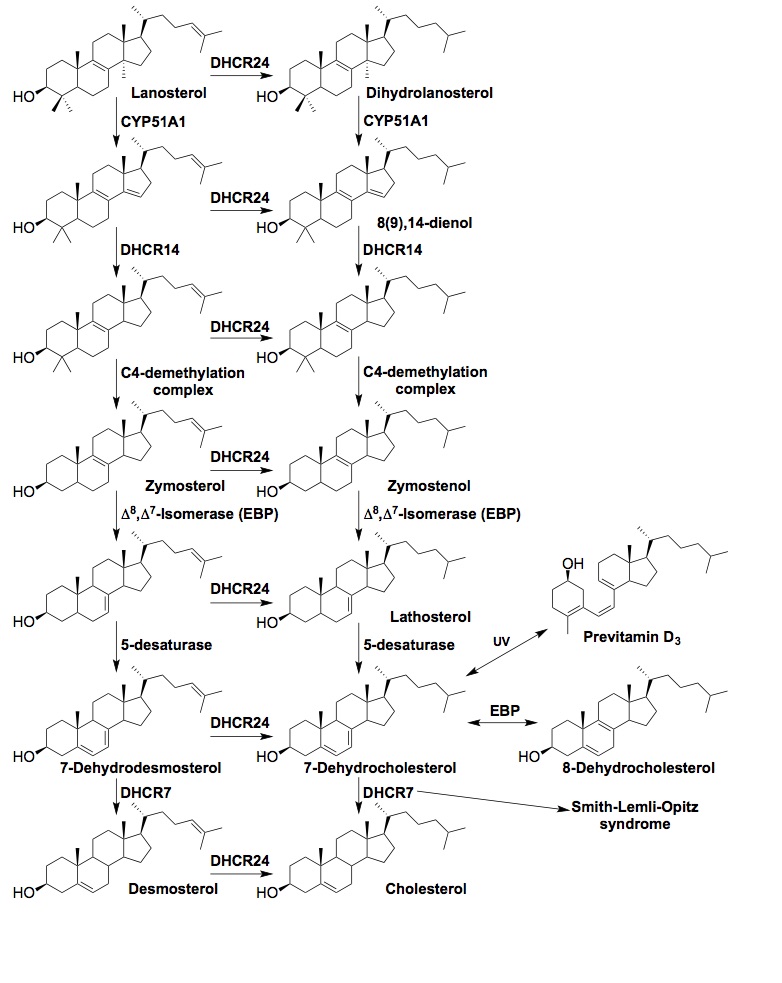
Cholesterol Biosynthesis Disorders
In the postsqualene cholesterol biosynthesis pathway, cyclization of squalene-2,3-epoxide gives the first sterol, lanosterol, which is followed by multi-step transformations, leading to the ultimate product cholesterol (See Figure below). Depending on whether the C24 double bond is reduced early or later by 3β-hydroxysterol-Δ24-reductase (DHCR24; EC 1.3.1.72), the pathway has been defined as the Kandutsch-Russell pathway (sequence on the right) or Bloch pathway (sequence on the left), respectively. Defects in each step of cholesterol biosynthesis causes a disorder, which results in accumulation of specific cholesterol precursors [1]. In the case of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome, the affected enzyme is 3β-hydroxysterol-Δ7-reductase (DHCR7; EC 1.3.1.21), leading to accumulation of 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC). Notably, 7-DHC also serves as the biosynthesis precursor to vitamin D3 in human skin, where ring-B is opened upon UV irradiation.
Reference
1. Porter, F. D., and Herman, G. E. (2011) Malformation syndromes caused by disorders of cholesterol synthesis, J. Lipid Res. 52, 6-34.