| Classification | Description | Notes |
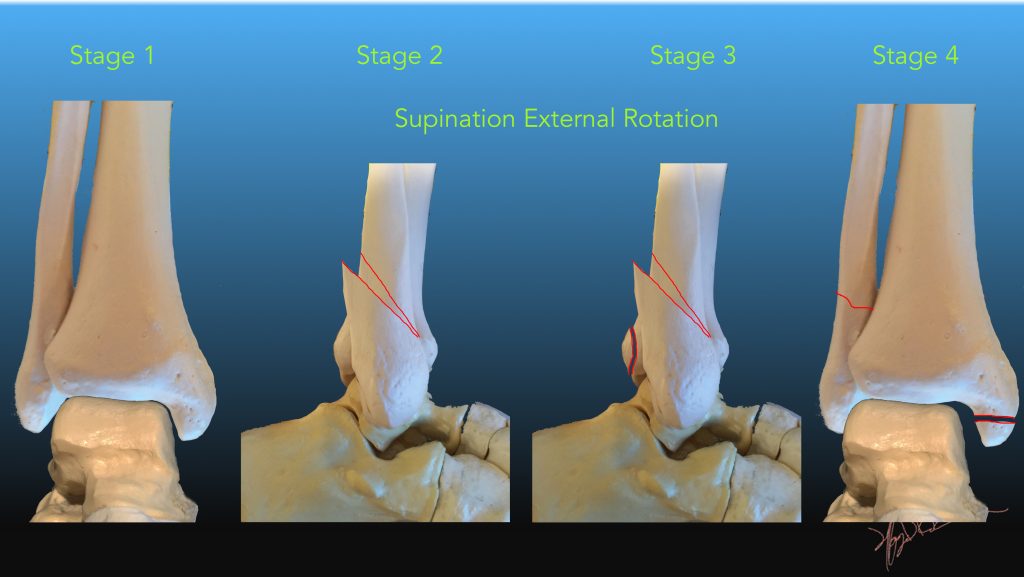
| Supination External Rotation | Most common mechanism (40-70% of all fractures) | |
| 1 | Anterior tibiofibular ligament rupture | Lateral malleolar soft tissue swelling. No fracture |
| 2 | Add lateral malleolar fracture
(Weber B) |
Low anterior, high posterior fracture plane |
| 3 | Add posterior tibiofibular ligament rupture or posterior malleolar fracture | |
| 4 | Add medial malleolar fracture or deltoid ligament rupture | |
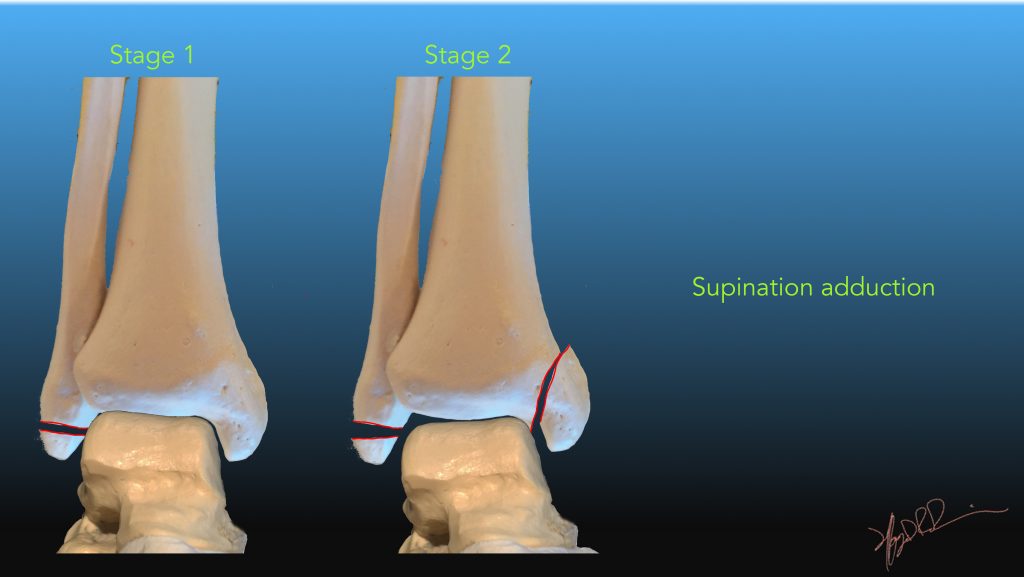
| Supination Adduction | Medial compression, lateral traction forces | |
| 1 | Lateral malleolus fracture (Weber A) | |
| 2 | Add vertical medial malleolus fracture | |
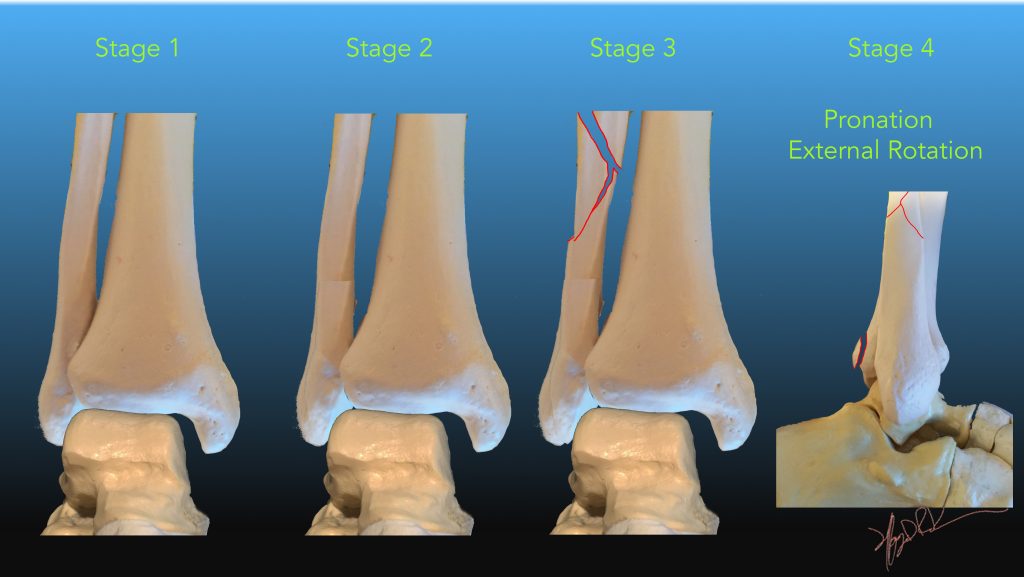
| Pronation External rotation | Deltoid ligament under stress in pronation. | |
| 1 | Deltoid ligament rupture
(medial mortise widening) |
|
| 2 | Add anterior tibiofibular ligament rupture | |
| 3 | Add spiral or oblique distal fibular fracture (Weber C) | |
| 4 | Add posterior tibiofibular ligament rupture, or posterior malleolar fracture | |
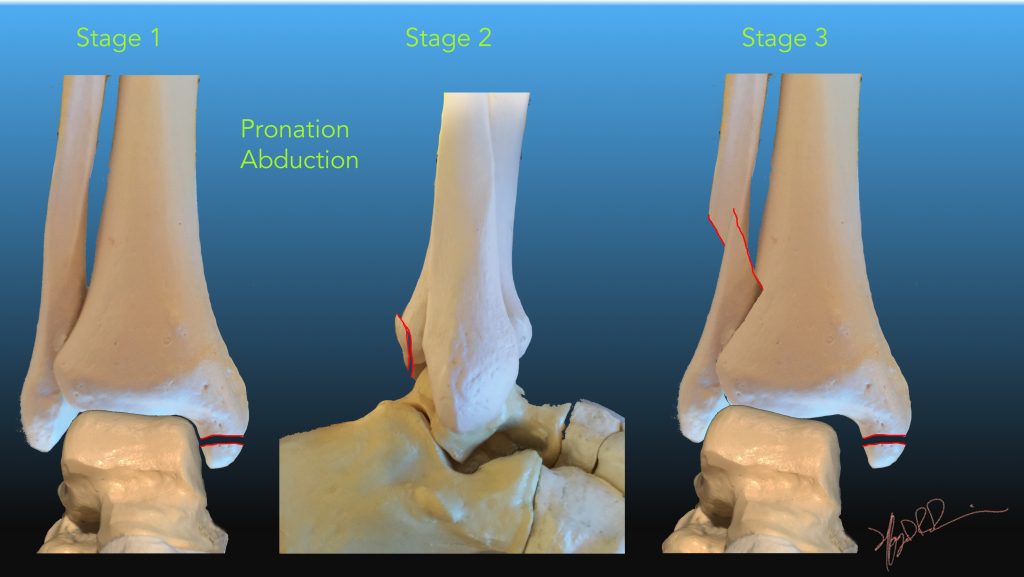
| Pronation Abduction | Deltoid ligament under stress in pronation. | |
| 1 | Deltoid ligament rupture or transverse medial malleolar fracture | |
| 2 | Add posterior malleolar fracture | |
| 3 | Add distal fibular fracture (Weber B) | High lateral, low medial fracture plane |
Foot position:
Supination- weight on lateral foot.
Pronation- weight on medial foot.
Abnormal forces:
Abduction- tilts lateral talus upwards.
Adduction- tilts medial talus upwards.
External rotation- outward rotation of the foot about the Z-axis
References:
Okanobo, H., et al. (2012). “Simplified diagnostic algorithm for Lauge-Hansen classification of ankle injuries.” Radiographics 32(2): E71-84.
