Lecture 31
Social 1
- Social Psychology
- Definition
- Principal Principles
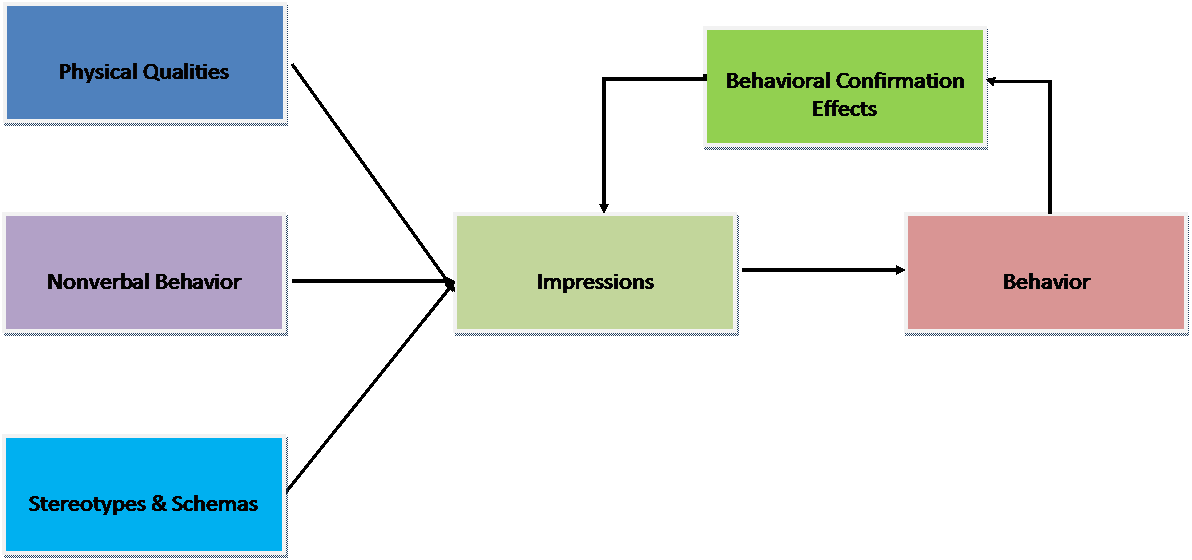
- First Impressions
- Primacy Effects
- Behavioral Confirmation Effects
- Attractiveness
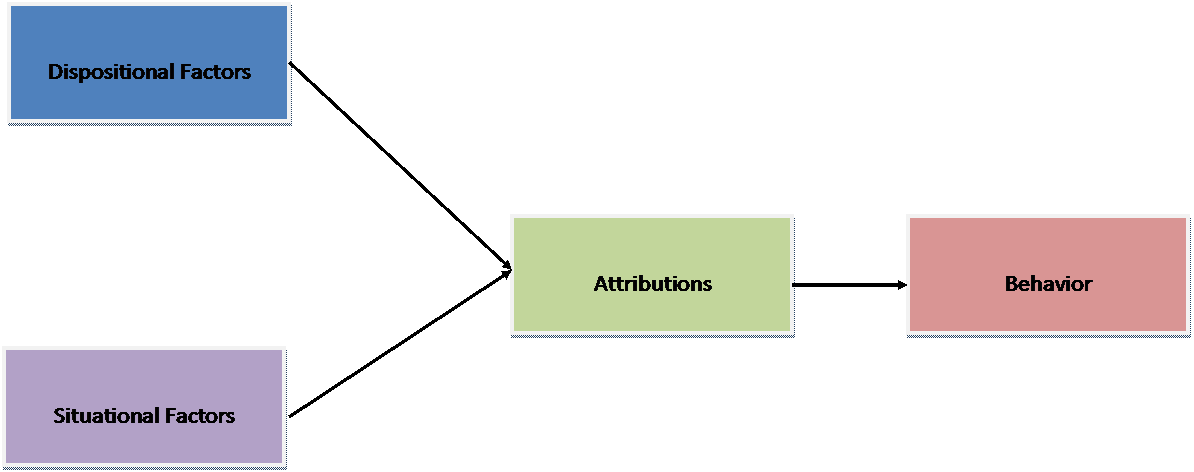
- Causal Attributions
- Definition
- Why why matters
- Heider's Theory
Overview
Social psychology is the scientific study of social life. The field is very broad and covers virtually all behaviors of an interpersonal nature, from altruism to violence. In this lecture I introduced the field, noting that social psychologists believe a person's behavior depends on what seems to be, rather than what is. Formally, this assumption is known as a phenomenological perspective. We then discussed two central topics in the field: (a) The process by which we form a first impression of a person and (b) the process by which we decide why people behave the way they do.
Specifics
- Define social psychology and identify its principal principles.
- Identify three factors that influence first impressions.
- Know what is meant by the term "primacy effect" in impression formation and be familiar with two reasons why it is thought to occur.
- Know the "what is beautiful is good" stereotype, and be familiar with how the perceived attractiveness of a face is influenced by the "averageness" of facial features and facial symmetry.
- Be familiar with behavioral confirmation effects and the process by which people can inadvertently confirm their opinion of others.
- Know Heider's "formula" for describing perceived behavior, and distinguish dispositional causes from situational ones.
Social Psychology's Principal Principles

Model of the Impression Formation Process
Attributions