For a sample of size
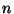
, two-sided critical values are given for significance levels .10, .05, and .01. Reject the null hypothesis of independence if the absolute value of the sample Spearman correlation coefficient exceeds the tabled value.
Table 1:
Critical values for Spearman's rank correlation coefficient.
| |
Two-sided 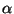 |
| |
.10 |
.05 |
.01 |
 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
.900 |
-- |
-- |
| 6 |
.829 |
.886 |
-- |
| 7 |
.714 |
.786 |
.929 |
| 8 |
.643 |
.738 |
.881 |
| 9 |
.600 |
.700 |
.833 |
| 10 |
.564 |
.648 |
.794 |
| 11 |
.536 |
.618 |
.818 |
| 12 |
.497 |
.591 |
.780 |
| 13 |
.475 |
.566 |
.745 |
| 14 |
.457 |
.545 |
.716 |
| 15 |
.441 |
.525 |
.689 |
| 16 |
.425 |
.507 |
.666 |
| 17 |
.412 |
.490 |
.645 |
| 18 |
.399 |
.476 |
.625 |
| 19 |
.388 |
.462 |
.608 |
| 20 |
.377 |
.450 |
.591 |
| 21 |
.368 |
.438 |
.576 |
| 22 |
.359 |
.428 |
.562 |
| 23 |
.351 |
.418 |
.549 |
| 24 |
.343 |
.409 |
.537 |
| 25 |
.336 |
.400 |
.526 |
| 26 |
.329 |
.392 |
.515 |
| 27 |
.323 |
.385 |
.505 |
| 28 |
.317 |
.377 |
.496 |
| 29 |
.311 |
.370 |
.487 |
| 30 |
.305 |
.364 |
.478 |