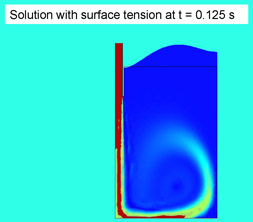
Microwell mixing with surface tension Nick Cox
For many applications in the pharmaceutical industry, achieving the rapid, homogeneous mixing of very small volumes can have a dramatic impact on the success or failure of a process. One method of achieving a homogeneous mixture in a small volume (for instance, a 200 micro liter well in a in a 96-well plate) is the repetitive injection and subsequent aspiration of a concentrated liquid through an automatic pipette. Although the amount and speed of mixing has been measured experimentally using dyes and other methods, a theoretical/computational approach has not yet been developed. This report describes an investigation into the ability of computational methods to model microwell mixing. In particular, this report builds on previous work, attempting to include a model for the surface tension of the fluid inside a microwell. |